2.6 数据库与数据文件
Created on Wed Sep 21 17:40:01 2022; Last updated on 2024-09-10T14:29:00+08:00 @author: Richie Bao
目前,GH 通常只存储几何信息及其相关属性数据,不适合于大量信息数据的存储和管理;同时,如果信息数据位于一个 GH 文件中,也不方便信息数据的查看、重复调用和修改;再者,与其它数据分析平台协同时,仍旧需要某种类型的数据文件作为中转;GH 不仅是参数化建模,也需要融入相关的分析内容,这包括设计前场地分析和设计后评估,或生成设计,往往需要数据信息的支持或将分析后的数据存入外部文件中。因此,需要在 GH 中读写相关数据库或者相关格式类型的数据文件。GH 自身提供了一些文件类型的读写组件,例如Import SHP、Import Coordinates、Import Image等。但是,这不能满足进一步的数据文件存储管理需求,一是,提供的组件读写数据文件类型有限;二是,提供的组件输出信息内容受到限制。就上述原因,自行构建数据读写组件,方便数据文件弹性管理、编辑、读写、存储和作为中转文件都是必要的。
数据存储的方式主要包含两类,一是,数据库;二是,数据文档。对于数据库,考虑使用SQLite①和PostgreSQL②,其中PostgreSQL数据库支持存储几何信息。对于数据文档,会根据具体的应用场景选择,例如没有格式规定的 TXT 文件,可以自行确定数据格式,再根据格式编写读写代码;已规定数据格式,方便数据交流的 CSV、JSON 格式数据和 Excel 等;及地理信息数据文件类型,例如 GeoJSON、Shapefile、KML 或 KMZ 等。
数据库和数据文件读写是为了管理、存储数据,并用于设计或分析中。Python Script 是面向三维平台建模的 Python 脚本编辑器,支持 Python 扩展库的安装,很多 Python 数据分析和机器学习库可以在 Python Script 中实现,例如NumPy、pandas、SciPy、statsmodels、scikit-learn等。而某些无法在 Python Script 中实现的功能也可以单独在 Anaconda ③等平台中进行数据分析,充分利用 Python 庞大的扩展库,避免从头造轮子。
2.6.1 SQLite 数据库
SQLite 是一种轻量级的关系型数据库管理系统,其无需服务器、自给自足、零配置、具有跨平台的 SQL(Structured Query Language)数据库引擎,非常方便数据库的迁移(类似普通文件的拷贝),广泛用于浏览器、嵌入式系统等小型应用程序中。
以将《环境景观——绿化种植设计》(图集号 03J012-2,同一编号 GJBT-599)信息(部分示例)转换为数据并存储到 SQLite 数据库,在 Python 和 Python Script 中实现读写为例。图集为扫描的图片格式,可以使用百度智能云④图文转换器等工具实现数字化,存储为 TXT 文本文件。为了方便在 Python 中实现文本信息的提取,可以在文本文件中增加辅助标识符,减轻 Python 代码编写的难度和复杂度。主要使用的符号包括:标识提取数据区段的######1s和#######1e,分别为数据提取的开始和结束,其中数字1可以根据不同提取区段转换为其它的数字;标识标题(字段)的$,例如:
1.4.6Ⅶ区代表城市广州
######1s
$落叶灌木:
木芙蓉(625)、木槿(626)、紫荆(402)、郁李(469)、笑靥花(441)、珍珠花(442)、麻叶绣线菊(445)、菱叶绣线菊(448)、现代月季(497)、糯米条(593)、石榴(410)、紫珠(588)、紫玉兰(271)、胡枝子(390)、金银木(597)、木本绣球(610)、蝴蝶树(614)、接骨木(608)、无花果(422)、花椒(377)、枸桔(378)、醉鱼草(585)、小蜡(583)
$竹类:
青皮竹(646)、慈竹(667)、粉单竹(648)、箬竹(642)、苦竹(664)、孝顺竹(643)、凤尾竹(644)、毛竹(658)、淡竹(661)、黄金间碧玉竹(650)、佛肚竹(649)、麻竹(Dendrocalamuslatiflorus)
#######1e
植物群落示例:
######2s
1、小叶榕+榄树+朴树+假萍婆一散尾葵一春羽+艳山姜
2、红花羊蹄甲—山茶—海芋+艳山姜一地毯草
3、白兰一油茶+大头菜一虎尾兰
12、火力楠+红花木莲一含笑+夜合+厚皮香一蚌花
#######2e
2.1生态性状
######3s
$阴性树种
偃松(20)、东北红豆杉(61)、矮紫杉(62)、三尖杉(69)、含笑(83)、中国地锦(694)、洒金东瀛珊瑚(168)、阔叶十大功劳(117)、十大功劳(118)、红背桂(161)、中华常春藤(705)、常春藤(707)、八角金盘(215)、鹅掌藤(706)、紫金牛(Ardisia japonica )、朱砂根(Ardisia crenata )、络石(709)、六月雪(226)、春羽(715)、麒麟尾(713)、心叶蔓绿绒(716)、矮棕竹(255)、筋头竹(256)、三药槟榔(242)
$耐盐碱树种
黑松(16)、侧柏(35)、木麻黄(234)、柽柳(522)、新疆杨(292)、箭杆杨(295)、钻天杨(297)、胡杨(301)、小叶杨(294)、桑(418)、杞柳(311)、白柳(310)、蒙古柳(312)、旱柳(305)、枸杞(587)、楝树(343)、大果榆(324)、榆树(326)、朴树(331)、火炬树(349)、毛泡桐(367)、臭椿(411)、刺槐(392)、紫穗槐(384)、皂荚(400)、国槐(396)、绒毛白蜡(556)、桂香柳(534)、杜梨(491)、合欢(379)、枣(510)、杏(465)、君迁子(549)、金焰绣线菊(446)、金山绣线菊(447)、花红(458)、海棠果(460)、西府海棠(462)、椰子(248)、水椰(Nypafruticans )
#######3e
各区划常用木本园林植物性状表则转换为 Excel 电子表格(表 2.6-1)。
表 2.6-1 各区划常用木本园林植物性状表
| 序号 | 中名 | 学名 | 科名 | 高度(m) | 适用地区 | 生态习性 | 生物学特性及观赏特性 | 园林用途 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 苏铁 | Cycas revolute | 苏铁科 | 2 | 华南、西南(VⅦ、D | 中性,喜暖热湿润气候及酸性土 | 花黄褐色7~8月,姿态优美 | 景园树 |
| 2 | 南洋杉 | Araucaria cunninghamii | 南洋杉科 | 20~30 | 华南(Ⅶ南部、Ⅷ) | 阳性,喜暖热气候,不耐寒,喜肥,生长快 | 树冠狭圆锥形,姿态优美 | 风景树、行道树 |
| 3 | 异叶南洋杉 | Araucaria heterophylla | 南洋杉科 | 10~30 | 华南(Ⅶ南部、Ⅷ) | 阳性,喜暖热气侯,不耐寒,喜肥,生长快 | 树冠塔形 | 风景树、行道树 |
| 4 | 辽东冷杉 | Abies holophylla | 松科 | 30 | 东北东南部、华北(Ⅱ、Ⅲ) | 阴性,喜冷凉湿润气候,酸性土,耐寒 | 树冠圆锥形 | 风景林、庭荫树 |
| 5 | 臭冷杉 | Abies nephrolepis | 松科 | 30 | 东北及华北山地(Ⅱ、Ⅲ) | 阴性,喜冷湿环境及酸性土壤,浅根性 | 树冠尖塔形 | 风景林、用材林 |
| 6 | 日本冷杉 | Abies firma | 松科 | 30-40 | 华东、华中(IV-VD | 阴性,喜冷凉湿润气候及酸性土 | 树冠圆锥形 | 风景林、用材林 |
| 7 | 青海云杉 | Picea carassifolia | 松科 | 23 | 西北(Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅸ) | 中性,浅根性 | 树冠塔形 | 风景林、行道树、景园树 |
| 8 | 青杆 | Picea wilsonii | 松科 | 50 | 西北、华北、东北(Ⅱ、Ⅲ、) | 耐阴性强,喜凉爽湿润气候,适应力强,喜微酸性土壤 | 针叶灰蓝色,枝叶繁密 | 风景林、景园树 |
| 9 | 白杆 | Picea meyeri | 松科 | 30 | 华北、东北、山西、河南(Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅸ) | 中性,耐阴,喜冷凉湿润气候,生长慢 | 树冠圆锥形,针叶粉蓝色 | 风景林、景园树 |
| 10 | 云杉 | Picea asperata | 松科 | 45 | 陕、甘、晋、宁、川北(IⅣ-V西部) | 中性,耐阴,喜凉润气候及排水良好的酸性土壤,耐干冷,浅根性 | 冠圆锥形,叶灰绿色 | 园景树及风景树、用材林 |
| 11 | 红皮云杉 | Picea koraiensis | 松科 | 30 | 东北、华北(Ⅱ、Ⅲ) | 耐阴,耐干旱,耐寒,生长较快 | 树冠圆锥形 | 园景树 |
| 12 | 欧洲云杉 | Picea abies | 松科 | 36~60 | 华东(II~VI东部) | 喜温凉气候及深厚湿润的酸性土 | 针叶鲜绿色 | 园景树,常用作圣诞树和用于岩石园 |
| 13 | 樟子松 | Pinus sylvestris | 松科 | 30 | 东北、西北(I、IⅡ、Ⅸ、Ⅹ) | 强阳性,耐寒、耐干旱耐瘠薄,深根性,抗风沙 | 针叶黄绿色 | 防护林、风景林 |
| 14 | 油松 | Pinus tabulaeformis | 松科 | 10~30 | 东北南部,华北、西北(IIⅢ、Ⅳ、Ⅸ) | 强阳性,耐寒、耐干旱耐瘠薄,深根性 | 老年树冠伞形,树姿苍劲古雅,枝繁叶茂 | 庭荫树、风景林、防护林、行道树 |
2.6.1.1 在 Python 中读写 SQLite 数据库
读取文本文档定义的vegetation_database模块如下,其中gjbt599_text_extraction_A()函数用于提取区段1和3类型格式的文本文件。gjbt599_text_extraction_B()函数用于读取区段2类型格式的文本文件。Excel电子表格的读取可以使用pandas库提供的read_excel方法。
其中from database import df2SQLite,SQLite2df调用了自定义模块database中 DataFrame 格式数据读写 SQLite 数据库的函数。
vegetation_database.py模块
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from database import df2SQLite, SQLite2df
import pandas as pd
import re
flatten_lst = lambda lst: (
[m for n_lst in lst for m in flatten_lst(n_lst)]
if type(lst) is list
else [lst]
)
def gjbt599_text_extraction_A(txt_fn, s_mark, e_mark):
"""
示例区段1,3文本文件格式信息提取方式,包括区段标识符和标题符,例如:
######1s
$落叶灌木:
木芙蓉(625)、木槿(626)、紫荆(402)
$竹类:
青皮竹(646)、慈竹(667)
#######1e
Parameters
----------
txt_fn : string
文本文档路径名.
s_mark : string
提取区段开始标识符,例如######1s,######3s等.
e_mark : string
提取区段结束标示符,例如#######1e,#######3e等.
Returns
-------
veg_data_df : DataFrame
返回提取的 DataFrame 格式数据,字段包含:index(为默认生成索引)、category(为标题转化)、name(为树种名提取)和 idx(小括号内的树种索引).
"""
i = 0
start = False
key = ""
veg_data = []
mark = ""
pattern_idx = re.compile("\((.+?)\)")
pattern_name = re.compile("(.+?)\(")
with open(txt_fn, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
print(f"line------------------------------{i}", end="\r")
if line == s_mark:
start = True
continue
elif line == e_mark:
break
if start:
# print(line)
if line and line[0] == "$":
key = line[1:].split(":")[0]
else:
line_split = line.split("、")
# print(line_split)
try:
line_data = [
pattern_name.findall(i) + pattern_idx.findall(i)
for i in line_split
]
if key and any(line_data):
line_data = [
[key, i[0].strip(), i[1].strip()] for i in line_data
]
veg_data.extend(line_data)
except:
pass
i += 1
veg_data_df = pd.DataFrame(veg_data, columns=["category", "name", "idx"])
return veg_data_df
def gjbt599_text_extraction_B(txt_fn, s_mark, e_mark):
"""
示例区段2文本文件格式信息提取方式,包括区段标识符,例如:
######2s
1、小叶榕+榄树+朴树+假萍婆一散尾葵一春羽+艳山姜”的行数据
12、火力楠+红花木莲一含笑+夜合+厚皮香一蚌花
#######2e
Parameters
----------
txt_fn : string
文本文档路径名.
s_mark : string
提取区段开始标识符,例如######2s,######5s等.
e_mark : string
提取区段结束标示符,例如#######2e,#######5e等.
Returns
-------
veg_data_df : DataFrame
返回提取的 DataFrame 格式数据,字段为数字索引,每一列为一组群落植被.
"""
i = 0
veg_data = []
start = False
with open(txt_fn, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
print(f"line------------------------------{i}", end="\r")
if line == s_mark:
start = True
continue
elif line == e_mark:
break
if start:
line_lst = re.split("一|—", line)
line_lst = [i.split("、")[-1] for i in line_lst]
line_lst = [i.split("+") for i in line_lst]
line_lst = [
[f"{i}-" + j for j in line_lst[i]]
for i in range(len(line_lst))
]
line_lst = flatten_lst(line_lst)
veg_data.append(line_lst)
i += 1
veg_data_df = pd.DataFrame(veg_data).T
return veg_data_df
if __name__ == "__main__":
gjbt599_SQLite_fp = "../database/gjbt599_SQLite.sqlite"
txt_fn = r"../data/vegetation_guangzhou.txt"
# A - Ⅶ区代表城市广州 - 常用园林植物及人工配置植物群落
gjbt599_veg_text_zoning_representative = gjbt599_text_extraction_A(
txt_fn, "######1s", "#######1e"
)
df2SQLite(
gjbt599_SQLite_fp,
gjbt599_veg_text_zoning_representative,
"veg_zone_repr",
method="replace",
)
# B - 植物群里示例
gjbt599_veg_biome = gjbt599_text_extraction_B(
txt_fn, "######2s", "#######2e"
)
df2SQLite(
gjbt599_SQLite_fp, gjbt599_veg_biome, "veg_biome", method="replace"
)
# C - 生态性状
gjbt599_veg_ecological_traits = gjbt599_text_extraction_A(
txt_fn, "######3s", "#######3e"
)
df2SQLite(
gjbt599_SQLite_fp,
gjbt599_veg_ecological_traits,
"veg_ecological_traits",
method="replace",
)
# D-读取植物形状表
veg_traits_table_fn = "../data/vegetation_traits_table.xlsx"
veg_traits_table = pd.read_excel(veg_traits_table_fn, index_col=0)
df2SQLite(
gjbt599_SQLite_fp,
veg_traits_table,
"veg_traits_table",
method="replace",
)
数据库读写方法主要调用 Pandas 库提供的read_sql_table和to_sql方法。为了方便数据库读写参数的配置,尤其对engine数据库文件路径变量格式的定义,将其在函数内实现,简化数据库读写中输入参数的复杂程度。
database.py模块
def df2SQLite(db_fp,df,table,method='fail'):
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
'''
function - pandas 方法,把 DataFrame 格式数据写入数据库(同时创建表)
Paras:
db_fp - 数据库文件路径
df - 待写入数据库的DataFrame格式数据
table - 表名称
method - 写入方法,'fail','replace'或'append'
'''
engine=create_engine('sqlite:///'+'\\\\'.join(db_fp.split('\\')),echo=True)
try:
df.to_sql(table,con=engine,if_exists="%s"%method)
if method=='replace':
print("_"*10,'the %s table has been overwritten...'%table)
elif method=='append':
print("_"*10,'the %s table has been appended...'%table)
else:
print("_"*10,'the %s table has been written......'%table)
except:
print("_"*10,'the %s table has been existed......'%table)
def SQLite2df(db_fp,table):
import pandas as pd
'''
function - pandas 方法,从 SQLite 数据库中读取表数据
Paras:
db_fp - 数据库文件路径
table - 所要读取的表
'''
return pd.read_sql_table(table, 'sqlite:///'+'\\\\'.join(db_fp.split('\\'))) #pd.read_sql_table从数据库中读取指定的表
使用DB Browser for SQLite(DB4S)⑤查看 SQLite 数据库,例如查看表名为"veg_biome"的群落,如图 2.6-1。
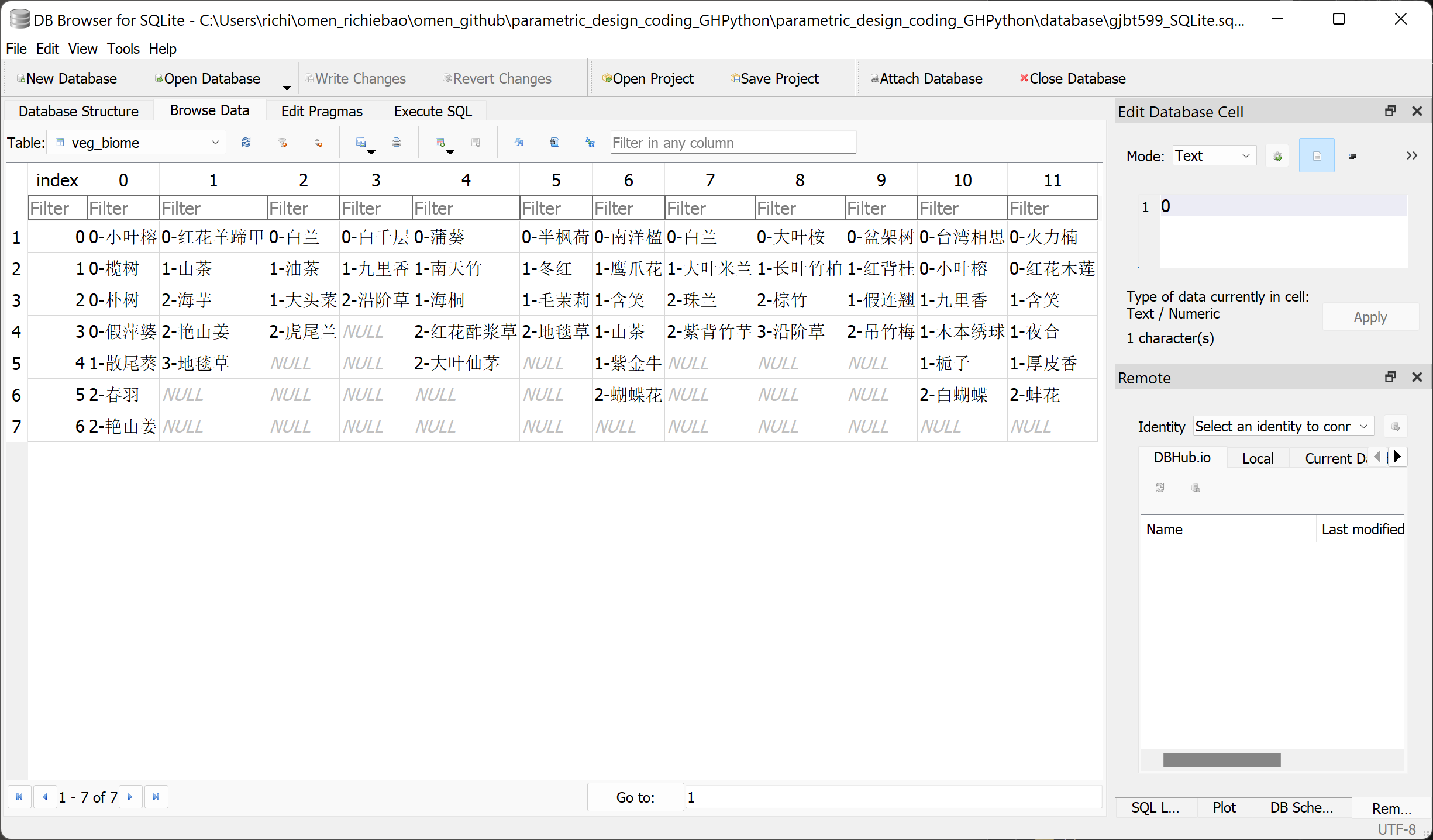
图 2.6-1 用 DB Browser for SQLite 工具查看数据库表
⇩vegetation_guangzhou.txt 数据文件下载
2.6.1.2 Python Scirpt 编写组件读写 SQLite 数据库文件
在 Python Script 中定义创建和读写 SQLite 数据库组件,使用sqlite3库实现。用 Python Script 定义了Create SQL_DB、SQL DB Dump和SQL DB Load3个组件,分别用于 SQLite 数据库的创建、写入和读取。
图 2.6-2 GH 代码,是读取了 Python 中写入到gjbt599_SQLite.sqlite数据库的表“veg_zone_repr”和“veg_biome”,并创建新数据库database_T,将读取的“veg_biome”表信息重写入到新建数据库中。写入时,因为字段index和整数字符字段值无法通过sqlite3创建表结构,因此配置输入参数Prefix为g_,修改字段名。
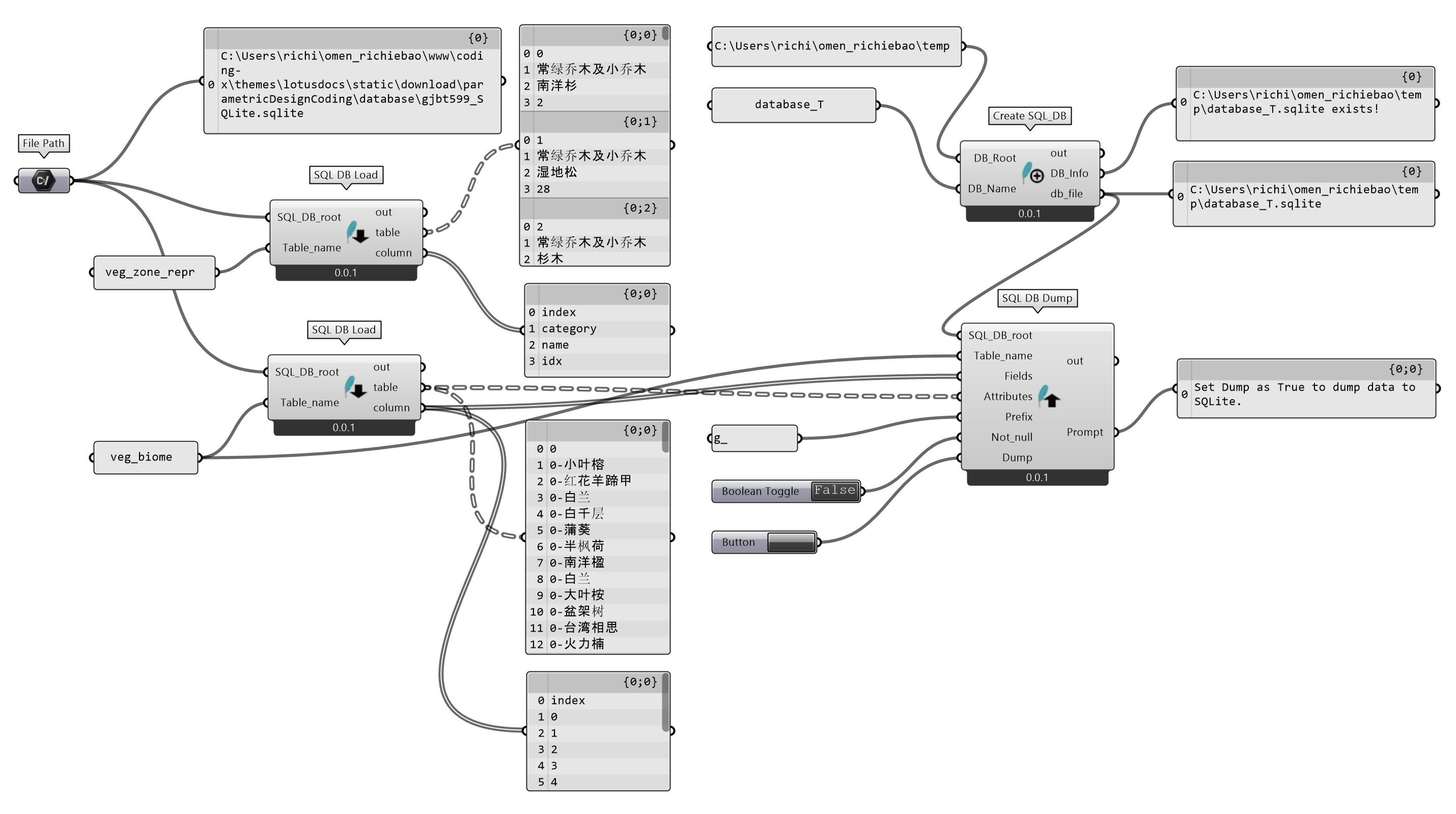
图 2.6-2 用 Python Script(GH)编写读写 SQLite 数据库组件
Create SQL_DB (Python Script 组件)
"""建立 SQLite 数据库
Inputs:
DB_Root: 数据库根目录。DS:Item Access;TH:str
DB_Name: 数据库名。DS:Item Access;TH:str
Output:
DB_Info: 数据库建立情况信息
db_file: 数据库文件路径"""
ghenv.Component.Name = "Create SQL_DB"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "Create SQL_DB"
ghenv.Component.Description = "Create SQL_DB"
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Database"
ghenv.Component.AdditionalHelpFromDocStrings = "1"
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import os
import sqlite3
from sqlite3 import Error
def create_connection(db_file):
"""创建 SQLite 数据库链接"""
conn = None
try:
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_file)
print(sqlite3.version)
return sqlite3.version
except Error as e:
print(e)
return e
finally:
if conn:
conn.close()
def create_sqlite_db(DB_Root, DB_Name):
"""
建立 SQLite 数据库
"""
db_file = os.path.join(DB_Root, DB_Name + ".sqlite")
if os.path.exists(db_file):
print("db_file exists!")
DB_Info = "{} exists!".format(db_file)
else:
info = create_connection(db_file)
DB_Info = "created {} database; sqlite_version={}".format(DB_Name, info)
return db_file, DB_Info
if __name__ == "__main__":
if DB_Root and DB_Name:
db_file, DB_Info = create_sqlite_db(DB_Root, DB_Name)
SQL DB Dump (Python Script 组件)
""" 从 SQLite 中读取表.
Inputs:
SQL_DB_root: SQLite 数据库路径;DS:Item Access;TH:str
Table_name: 表名。DS:Item Access;TH:str
Fields: 列名(字段名)。DS:List Access;TH:str
Attributes: 待写入的数据,每个样本一个列表,各个列名存储样本属性值。DS:Tree Access;TH:Default
Prefix: 字段名前缀,有时输入的字段名称可能无法用于表的创建,例如indx,或整数等,可以通过加入前缀修正。DS:Item Access;TH:str
Not_null:字段(列)是否可以为空,默认为可以。DS:Tree Access;TH:bool
Dump: 为True时将Attribute写入数据库。DS:Tree Access;TH:bool
Output:
Prompt: 写入提示"""
ghenv.Component.Name = "SQL DB Dump"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "SQL DB Dump"
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Database"
ghenv.Component.AdditionalHelpFromDocStrings = "1"
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import sqlite3
import ghpythonlib.treehelpers as th
from operator import itemgetter
Prompt = "Set Dump as True to dump data to SQLite."
def create_table(conn, sql_table, table_name):
"""
创建表
:param conn: Connection object
:param sql_table: a CREATE TABLE statement
"""
try:
c = conn.cursor()
c.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS %s" % table_name)
c.execute(sql_table)
except:
print("Something going wrong.")
def data2sqlite(conn, table_name, Fields, data):
"""
给定数据库连接,表名,字段名,将数据写入到数据库
"""
sql_values_base = """INSERT INTO {}(""".format(table_name)
for f in Fields:
sql_values_base = sql_values_base + "{},".format(f)
sql_values_base = sql_values_base[:-1] + ") VALUES (" + "?," * len(Fields)
sql_values = sql_values_base[:-1] + ")"
with conn:
data_ = [list(i) for i in zip(*data)]
conn.executemany(sql_values, data)
conn.commit()
def sqlite_dump(SQL_DB_root, Table_name, Fields, Attributes, Prefix, Not_null):
"""
数据写入到数据库主程序
"""
Attributes_lst = th.tree_to_list(Attributes)
Attributes_flip_lst = list(zip(*Attributes_lst))
data_type = [type(i) for i in list(map(itemgetter(0), Attributes_flip_lst))]
data_type_list = {str: "text", int: "integer", float: "real"}
Fields_type = [data_type_list[i] for i in data_type]
conn = sqlite3.connect(SQL_DB_root)
sql_table_base = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS {} ( id integer PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,""".format(
Table_name
)
if Prefix:
Fields = [Prefix + i for i in Fields]
for f, t in zip(Fields, Fields_type):
if Not_null:
sql_table_base += "{} {} NOT NULL,".format(f, t)
else:
sql_table_base += "{} {},".format(f, t)
sql_table = sql_table_base[:-1] + ");"
create_table(conn, sql_table, Table_name)
data2sqlite(conn, Table_name, Fields, Attributes_lst)
Prompt = "Data dumped."
if __name__ == "__main__":
if Dump:
sqlite_dump(
SQL_DB_root, Table_name, Fields, Attributes, Prefix, Not_null
)
QL DB Load (Python Script 组件)
"""从 SQLite 中读取表.
Inputs:
SQL_DB_root: SQLite 数据库路径。DS:Item Access;TH:str
Table_name: 表名。DS:Item Access;TH:str
Output:
table: 读取数据库中的表
column: 列名(字段名)"""
ghenv.Component.Name = "SQL DB Load"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "SQL DB Load"
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Database"
ghenv.Component.AdditionalHelpFromDocStrings = "1"
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import sqlite3
import ghpythonlib.treehelpers as th
import Rhino
def load_sqlite_db(SQL_DB_root, Table_name):
"""
指定数据库路径和表名,读取 SQLite 数据库文件
"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(SQL_DB_root)
with conn:
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("SELECT * FROM %s" % Table_name)
rows = cur.fetchall()
column = list(map(lambda x: x[0], cur.description))
layerTree = th.list_to_tree(
rows,
source=[
0,
],
)
table = layerTree
return table, column
if __name__ == "__main__":
if SQL_DB_root and Table_name:
table, column = load_sqlite_db(SQL_DB_root, Table_name)
2.6.2 PostgreSQL 数据库与 GeoJSON 地理空间信息数据交换格式
因为 GH(RH)主要服务于设计行业的三维模型建构,针对地理信息系统(Geographic Information System,GIS)的支持工具有限,且 GIS 的投影坐标系异于 RH 的三维直角坐标系,因此具有投影坐标的 GIS 几何往往远远偏离于 RH 的坐标原点。虽然相对坐标可以将其置于原点,但不能直观反映真实坐标系统和投影坐标数值,因此,对于涉及 GIS 的内容分析和地图显示仍然推荐直接在 Python 中处理或借助QGIS⑥等地理信息平台。
PostgreSQL 是一个开源的对象关系数据库系统(open source object-relational database system),可以存储具有投影坐标系统信息的地理空间数据,在 QGIS 等地理信息系统工具平台下可以直接从 PostgreSQL(PostGIS)中读入与显示数据,建立地图。PostgreSQL不同于SQLite,并不是单独的数据库文件形式,如果在本地电脑上建立PostgreSQL数据库需要安装pgAdmin⑦等工具辅助建立、查看和管理PostgreSQL数据库,例如在pgAdmin里 Databaes 下建立数据库名为ghpython,为了能够使该数据库存储具有坐标系统的地理几何对象的能力,需要在Query tool下执行CREATE EXTENSION postgis;命令。
2.6.2.1 Python 下的 JSON、GeoJSON 和读写 PostgreSQL 数据库
从Chicago Data Portal⑧或其它平台下载芝加哥城的建筑轮廓(含高度)数据,其存储格式为 JSON 文件。建立json2gpd()函数(置于json_geojson_postgresql模块),实现读取 JSON 文件数据并转换为 GeoDataFrame 格式数据。且建立读写PostgreSQL数据库的函数gpd2postSQL()和postSQL2gpd()(置于database模块),将建筑轮廓数据写入到新建的ghpython数据中,也单独存储为 GeoJSON 格式文件,供 Python Script 读取。
json_geojson_postgresql模块中定义的json2gpd()函数的参数mask,可以通过提供 Polygon 对象,用于按范围提取数据的操作。SHP(Shape)格式矢量数据通常保留 WGS84(World Geodetic System 1984)为 GPS 全球定位系统使用而建立的坐标系统。统一坐标系方便处理地理几何对象,但涉及距离计算等分析时,需要将其投影到对应的投影坐标系下,将单位度(经纬度)转换为米(长度)等单位。如果要将数据调入到 RH 中,一般也需要使用投影后的长度单位。
mask参数的范围数据是在Googel Earth Pro⑨中通过添加多边形工具绘制,并存储为单独的 KML 格式数据,然后在 Python 中使用GeoPandas库提供的read_file方法读取,配置driver='KML'。如果读取 KML 文件时提示没有KML驱动,则需要配置fiona.drvsupport.supported_drivers['KML']='rw'。
json_geojson_postgresql.py模块
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import geopandas as gpd
import pandas as pd
from database import gpd2postSQL, postSQL2gpd
import fiona
fiona.drvsupport.supported_drivers["KML"] = (
"rw"
)
def json2gpd(fp, epsg_original=None, epsg_target=None, mask=None):
"""
读取含有地理信息数据的 json 格式文件为 GeoDataFrame 格式数据
Parameters
----------
fp : string
json 文件路径.
epsg_original : int, optional
原始投影,epsg 编号. The default is None.
epsg_target : int, optional
转换为投影,epsg 编号. The default is None.
mask : polygon(Shapely), optional
提取的范围. The default is None.
Returns
-------
gdf : GeoDataFrame
转换后的数据.
"""
df = pd.read_json(fp)
gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_features(df["features"])
if epsg_original:
gdf.set_crs(epsg_original, inplace=True)
if mask:
mask_bool = gdf.within(mask)
gdf = gdf[mask_bool]
if epsg_target:
gdf.to_crs(epsg_target, inplace=True)
return gdf
if __name__ == "__main__":
# A-用于数据提取的边界
region4chicago_building_fp = "../data/region4chicago_building.kml"
region4chicago_building = gpd.read_file(
region4chicago_building_fp, driver="KML"
)
db_args = {
"myusername": "postgres",
"mypassword": "123456",
"mydatabase": "ghpython",
"geom_col": "geometry",
}
gpd2postSQL(region4chicago_building, table_name="region4chicago", **db_args)
# B-读取芝加哥区域 json 格式建筑地理信息数,并写入数据库和单独存储为 GeoJSON 地理数据格式
json_3DBuilding_fp = r"../data/Chicago_3dbuildings.json"
building_gpd = json2gpd(
json_3DBuilding_fp,
4326,
32616,
region4chicago_building.geometry.values[0],
)
gpd2postSQL(building_gpd, table_name="chicago_building_mask", **db_args)
building_gpd.to_file("../data/chicago_building.geojson", driver="GeoJSON")
database.py模块
def gpd2postSQL(gdf, table_name, **kwargs):
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
"""
function - 将 GeoDataFrame 格式数据写入 PostgreSQL 数据库
Paras:
gdf - GeoDataFrame 格式数据,含 geometry 字段(几何对象,点、线和面,数据值对应定义的坐标系统)
table_name - 写入数据库中的表名
**kwargs - 连接数据库相关信息,包括 myusername(数据库的用户名),mypassword(用户密钥),mydatabase(数据库名)
"""
engine = create_engine(
"postgresql://{myusername}:{mypassword}@localhost:5432/{mydatabase}".format(
myusername=kwargs["myusername"],
mypassword=kwargs["mypassword"],
mydatabase=kwargs["mydatabase"],
)
)
gdf.to_postgis(
table_name,
con=engine,
if_exists="replace",
index=False,
)
print("_" * 50)
print(
"The GeoDataFrame has been written to the PostgreSQL database.The table name is {}.".format(
table_name
)
)
def postSQL2gpd(table_name, geom_col="geometry", **kwargs):
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
import geopandas as gpd
"""
function - 读取 PostgreSQL 数据库中的表为 GeoDataFrame 格式数据
Paras:
table_name - 待读取数据库中的表名
geom_col='geometry' - 几何对象,常规默认字段为'geometry'
**kwargs - 连接数据库相关信息,包括myusername(数据库的用户名),mypassword(用户密钥),mydatabase(数据库名)
"""
engine = create_engine(
"postgresql://{myusername}:{mypassword}@localhost:5432/{mydatabase}".format(
myusername=kwargs["myusername"],
mypassword=kwargs["mypassword"],
mydatabase=kwargs["mydatabase"],
)
)
gdf = gpd.read_postgis(table_name, con=engine, geom_col=geom_col)
print("_" * 50)
print(
"The data has been read from PostgreSQL database. The table name is {}.".format(
table_name
)
)
return gdf
⇩json_geojson_postgresql.py 模块下载
⇩region4chicago_building.kml 边界数据下载
⇩Chicago_3dbuildings.json 建筑高度数据下载
将建筑轮廓数据写入数据库后,可以通过 pgAdmin 查看(图 2.6-3 )。同时也写入了用于数据提取的边界数据region4chicago。通常在地理信息数据处理分析时,地理信息数据和相关分析用数据都会预先处理后再写入到PostgreSQL数据库,方便数据管理和中转调用。
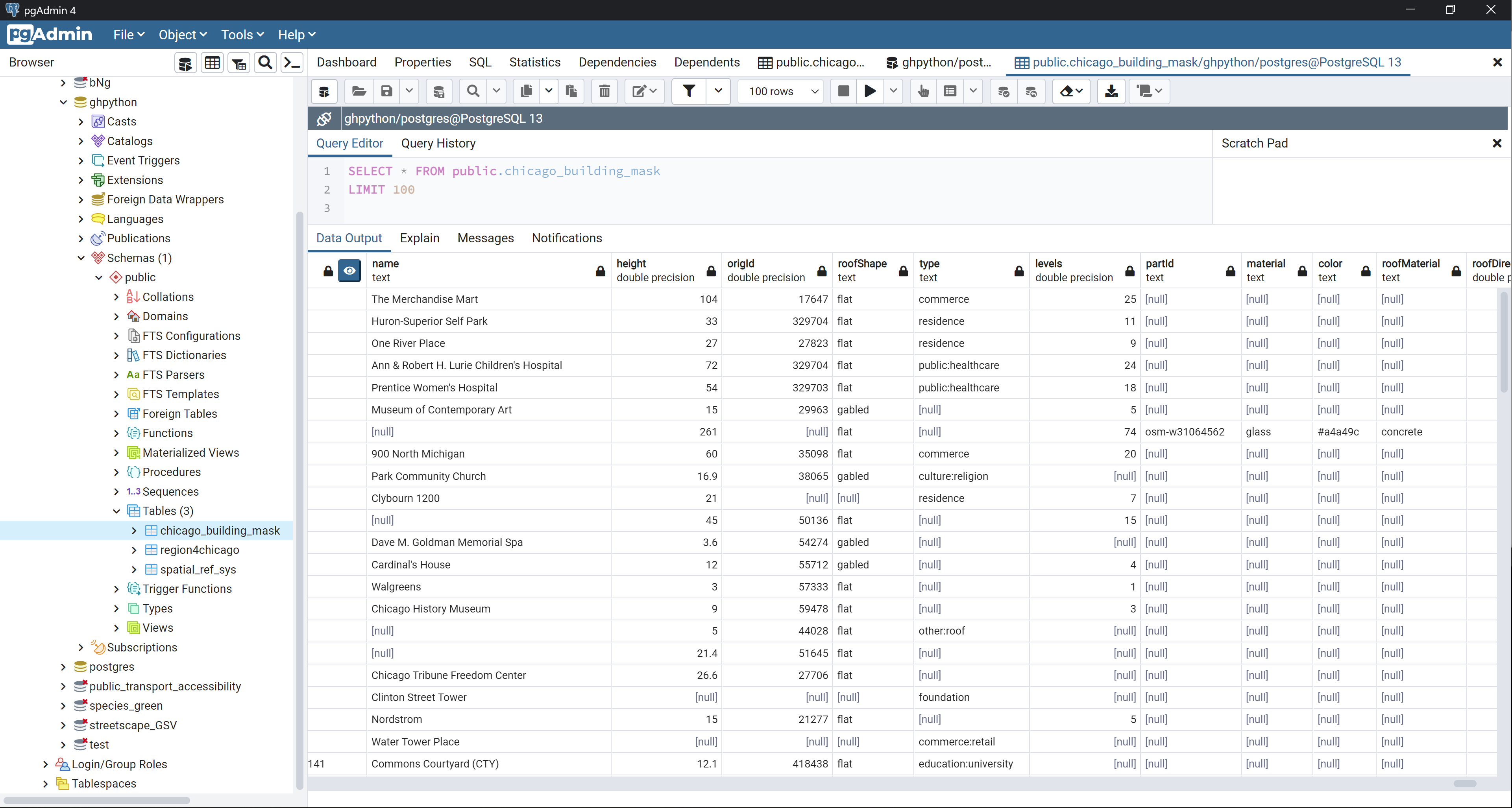
图 2.6-3 在 pgAdmin 中查看数据
QGIS 连接到数据库ghpython,读取显示地图(图 2.6-4)。
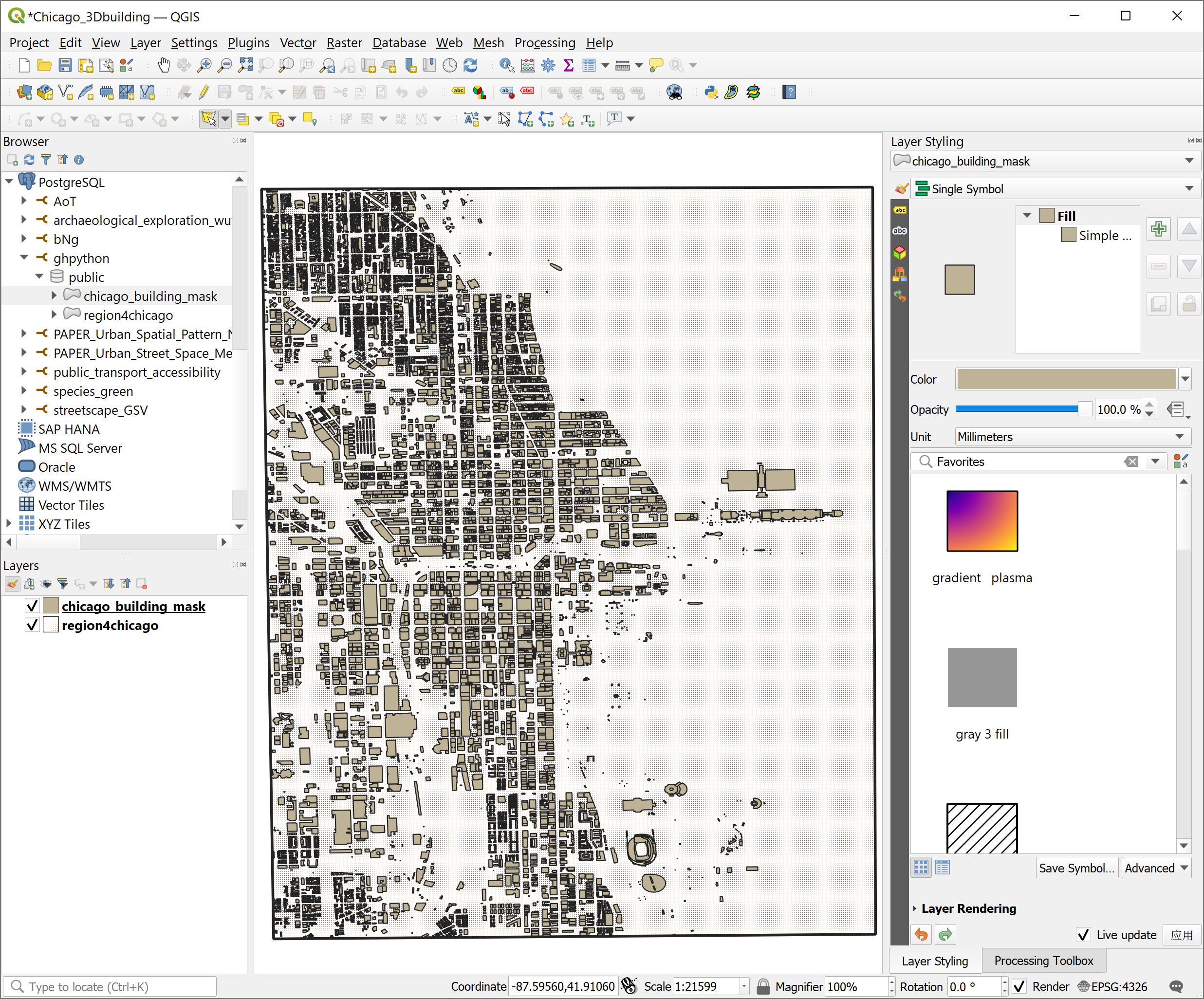
图 2.6-4 在 QGIS 中查看地图
2.6.2.2 在 Python Script 下读取 GeoJSON 数据
使用 Python Script 定义读取 GeoJSON 文件的Read GeoJSON组件(图 2.6-5)。在定义读写 GeoJSON 文件时,需要查看确定数据格式⑩,根据格式书写提取和构建格式代码,如下所示。
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": [
{
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [102.0, 0.5]
},
"properties": {
"prop0": "value0"
}
},
{
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "LineString",
"coordinates": [
[102.0, 0.0], [103.0, 1.0], [104.0, 0.0], [105.0, 1.0]
]
},
"properties": {
"prop0": "value0",
"prop1": 0.0
}
},
{
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "Polygon",
"coordinates": [
[
[100.0, 0.0], [101.0, 0.0], [101.0, 1.0],
[100.0, 1.0], [100.0, 0.0]
]
]
},
"properties": {
"prop0": "value0",
"prop1": { "this": "that" }
}
}
]
}
几何部分的定义包括基本几何对象(Geometry primitives),包含点(Point)、线(LineString)和面(Polygon),如表 2.6-2。复合几何(Multipart geometries ),包含多点(MultiPoint)、多线(MultiLineString)、多面(MultiPolygon)和多类(GeometryCollection),如表 2.6-3。几何对象的表达方式具体如表。
表 2.6-2 Geometry primitives
| Type | Graphic | Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
Point |
|
|
|
LineString |
|
|
|
Polygon |
|
|
|
|
|
表 2.6-3 Multipart geometries
| Type | Graphic | Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
MultiPoint |
|
|
|
MultiLineString |
|
|
|
MultiPolygon |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GeometryCollection |
|
|
存储为 GeoJSON 格式的建筑轮廓数据示例结构如下:
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"crs": { "type": "name", "properties": { "name": "urn:ogc:def:crs:EPSG::32616" } },
"features": [
{ "type": "Feature", "properties": { "name": "The Merchandise Mart", "height": 104.0, "origId": 17647.0, "roofShape": "flat", "type": "commerce", "levels": 25.0, "partId": null, "material": null, "color": null, "roofMaterial": null, "roofDirection": null, "minHeight": null, "roofHeight": null, "roofLevels": null, "roofColor": null, "minLevel": null, "shape": null }, "geometry": { "type": "Polygon", "coordinates": [ [ [ 447286.537477228150237, 4637545.708891036920249 ], ..., [ 447168.659624397521839, 4637637.741258095018566 ], [ 447169.095599453430623, 4637629.410504847764969 ], [ 447198.740866136853583, 4637577.004789265803993 ], [ 447216.252055328455754, 4637544.120034857653081 ], [ 447286.537477228150237, 4637545.708891036920249 ] ] ] } },
{ "type": "Feature", "properties": { "name": "Huron-Superior Self Park", "height": 33.0, "origId": 329704.0, "roofShape": "flat", "type": "residence", "levels": 11.0, "partId": null, "material": null, "color": null, "roofMaterial": null, "roofDirection": null, "minHeight": null, "roofHeight": null, "roofLevels": null, "roofColor": null, "minLevel": null, "shape": null }, "geometry": { "type": "Polygon", "coordinates": [ [ [ 448350.76425348961493, 4638380.651224782690406 ], ..., [ 448434.559148236527108, 4638381.709118346683681 ], [ 448350.76425348961493, 4638380.651224782690406 ] ] ] } },
{ "type": "Feature", "properties": { "name": null, "height": null, "origId": null, "roofShape": null, "type": null, "levels": null, "partId": null, "material": null, "color": null, "roofMaterial": null, "roofDirection": null, "minHeight": null, "roofHeight": null, "roofLevels": null, "roofColor": null, "minLevel": null, "shape": null }, "geometry": { "type": "Polygon", "coordinates": [ [ [ 446669.652006328105927, 4640586.637885542586446 ], [ 446676.037443786801305, 4640586.590007678605616 ], [ 446676.082395322097, 4640592.585518554784358 ], [ 446669.696963246737141, 4640592.633396429009736 ], [ 446669.652006328105927, 4640586.637885542586446 ] ] ] } }
]
}
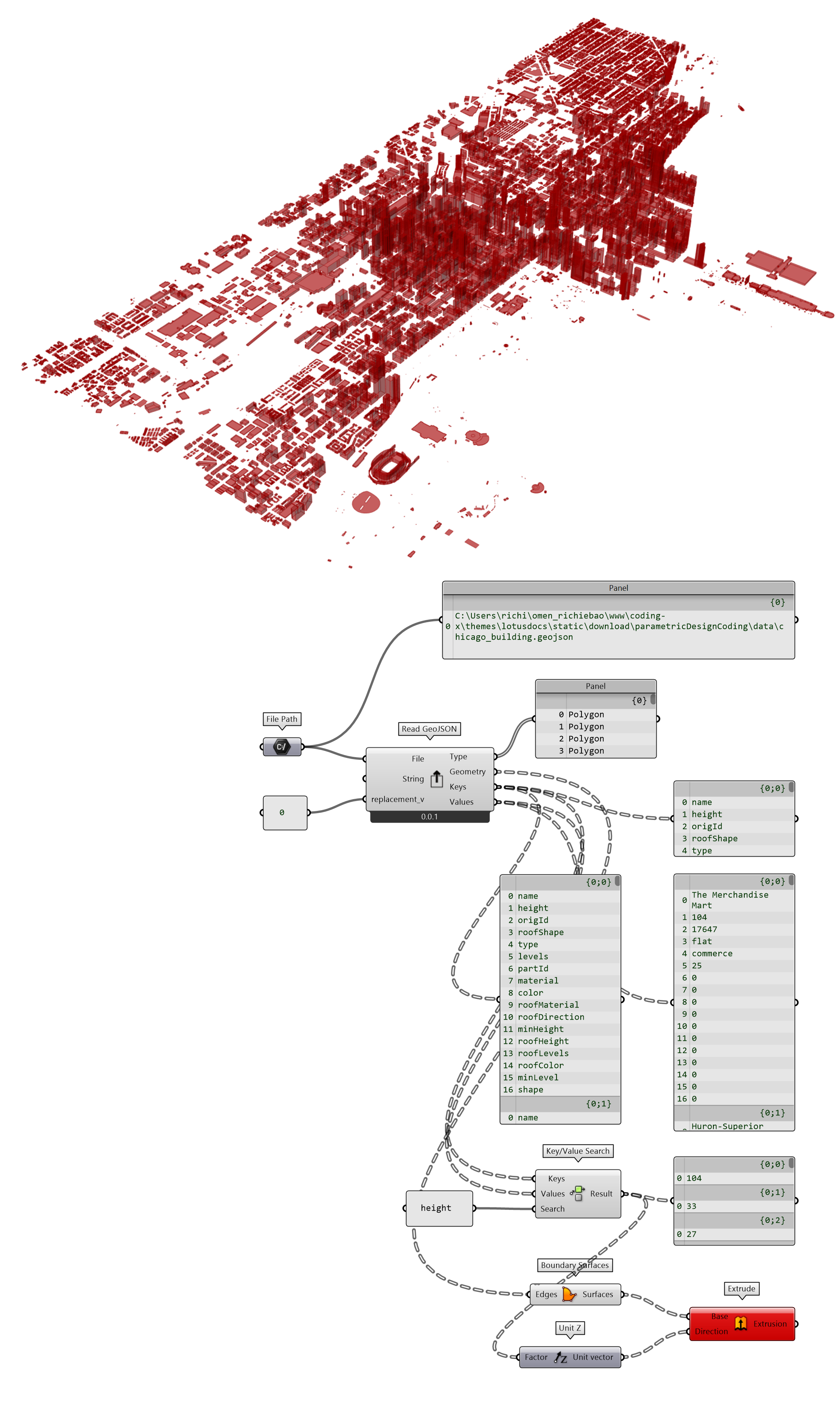
图 2.6-5 读取 GeoJSON 数据
Read GeoJSON (Python Script 组件)
"""读取 GeoJSON 数据
Inputs:
File: GeoJSON 文件路径. DS:Item Access;TH:str
String: 原始的 GeoJSON 字符串. DS:Item Access;TH:str
replacement_v:Null 替换值.DS:Item Access;TH:str
Output:
Type: GeoJSON 的原初类型.
Geometry: 变换为 Rhino 几何对象.
Keys: GeoJSON 属性键.
Values: GeoJSON 属性值"""
ghenv.Component.Name = "Read GeoJSON"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "Read GeoJSON"
ghenv.Component.Description = """Reads an GeoJSON file or raw GeoJSON string and translates it's contents into Rhino geometry"""
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Database"
ghenv.Component.AdditionalHelpFromDocStrings = "1"
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import ghpythonlib.treehelpers as th
def read_GeoJSON(file=None, string=None, replacement_v="9999"):
"""
读取 GeoJSON 地理空间信息数据交换格式文件
"""
if file:
with open(file, "r") as f:
geojson_string = f.read().strip()
elif string:
geojson_string = string
else:
geojson_string = None
if geojson_string:
type_lst = []
geometry_lst = []
keys_lst = []
values_list = []
if replacement_v:
geojson_string = geojson_string.replace("null", replacement_v)
geojson_dict = eval(geojson_string)
if "features" in geojson_dict.keys():
features = geojson_dict["features"]
else:
features = [geojson_dict]
for f in features:
type_g = f["geometry"]["type"]
coordinates = f["geometry"]["coordinates"]
properties = f["properties"]
keys = list(properties.keys())
values = list(properties.values())
# print(type_g,coordinates,keys,values)
if type_g == "MultiPolygon":
geometry = [
rs.AddPolyline(
[
rs.AddPoint([float(j[0]), float(j[1]), 0])
for j in i[0]
]
)
for i in coordinates
]
elif type_g == "Polygon":
geometry = [
rs.AddPolyline(
[rs.AddPoint([float(j[0]), float(j[1]), 0]) for j in i]
)
for i in coordinates
]
elif type_g == "MultiLineString":
geometry = [
rs.AddPolyline(
[rs.AddPoint([float(j[0]), float(j[1]), 0]) for j in i]
)
for i in coordinates
]
elif type_g == "MultiPoint":
geometry = [
rs.AddPoint([float(i[0]), float(i[1]), 0])
for i in coordinates
]
else:
print("The data format does not meet the requirements.")
type_lst.append(type_g)
geometry_lst.append(geometry)
keys_lst.append(keys)
values_list.append(values)
type_tree = th.list_to_tree(type_lst)
geometry_tree = th.list_to_tree(geometry_lst)
keys_tree = th.list_to_tree(keys_lst)
values_tree = th.list_to_tree(values_list)
return type_tree, geometry_tree, keys_tree, values_tree
else:
return [None] * 4
if __name__ == "__main__":
if replacement_v:
Type, Geometry, Keys, Values = read_GeoJSON(File, String, replacement_v)
else:
Type, Geometry, Keys, Values = read_GeoJSON(File, String)
2.6.2.3 在 Python Script 下写入 GeoJSON 数据
定义有4类 GeoJSON 格式数据组件,分别为写入点Feature from Points,写入线Feature from Lines,写入面Feature from Polygons和写入具有拓扑关系的面Feature from Polygons(+),及各类型的合并组件Join GeoJSON和最终写入组件Write File。同时,使用定义的Read GeoJSON组件读取写入的 GeoJSON 文件,验证结果(图 2.6-6)。
为了方便解释应用场景和组件功用,使用自定义Moths模组下的建筑布局_简版组件随机生成建筑组合。
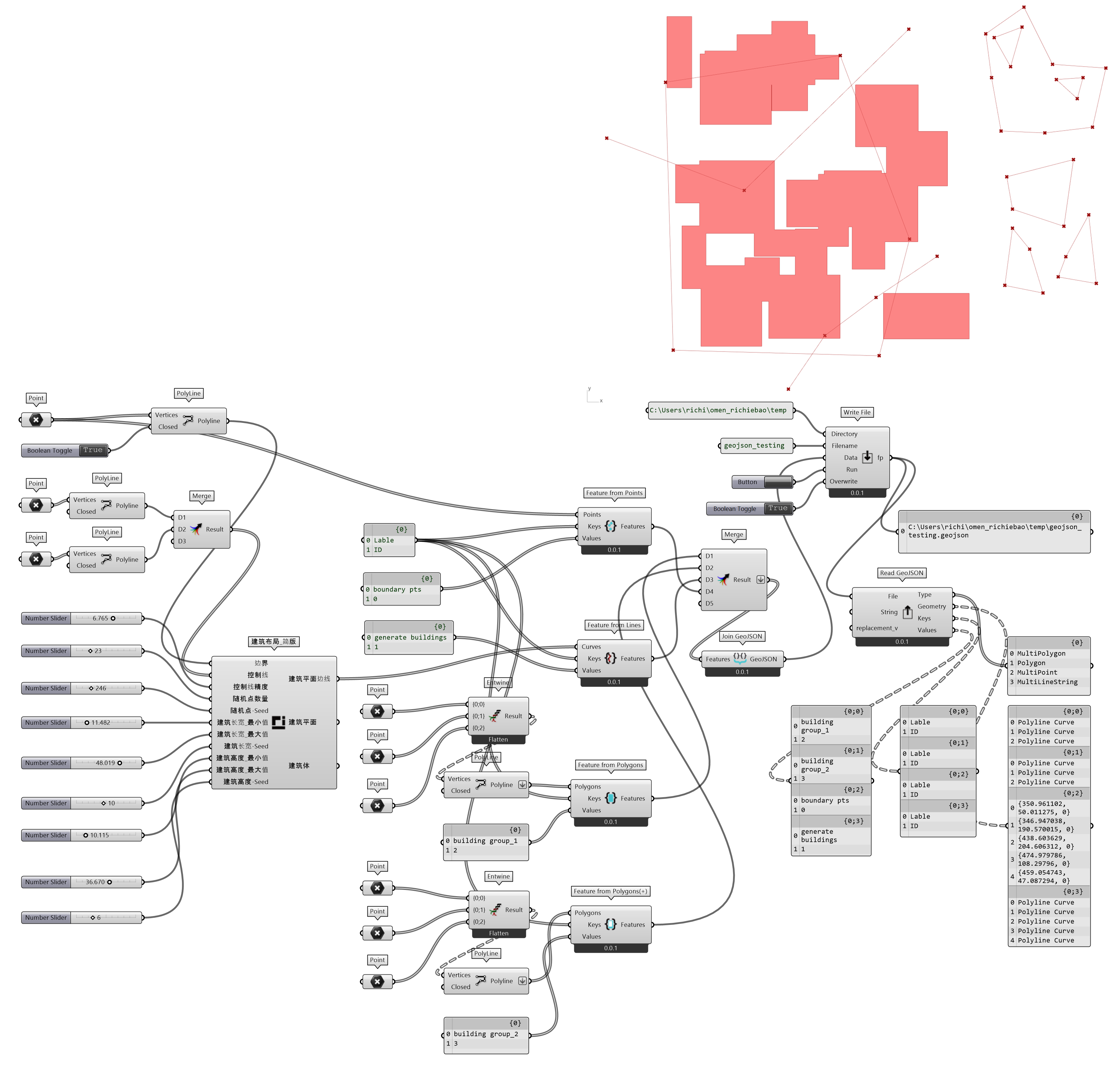
图 2.6-6 数据写入 GeoJSON 文件
Feature from Points (Python Script 组件)
"""建立 GeoJSON 点数据
Inputs:
Points: Points you want to export (One branch for each feature). DS:List Access;TH:Default
Keys: Keys to be save in object properties (One branch per feature). DS:List Access;TH:str
Values: Values to save in object properties (One branch per feature). DS:List Access;TH:str
Output:
Features: Strings containing GeoJSON geometry features (not a complete GeoJSON FeatureCollection yet, merge them via Join GeoJSON component). """
ghenv.Component.Name = "Feature from Points"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "Feature from Points"
ghenv.Component.Description = """Converts points into Point GeoJSON features and list of points into MultiPoint features."""
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Database"
ghenv.Component.AdditionalHelpFromDocStrings = "1"
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
def feature_from_points(points, keys, values):
properties = dict(zip(keys, values))
pts = []
for p_ in points:
if rs.IsPoint(p_):
p = rs.PointCoordinates(p_)
pts_coordi = [p.X, p.Y]
pts.append(pts_coordi)
geojson_dict_string = (
'{"type":"Feature","geometry":{"type":"MultiPoint","coordinates":%s},"properties":%s}'
% (pts, properties)
)
return geojson_dict_string.replace("'", '"')
if __name__ == "__main__":
if Points and Keys and Values:
Features = feature_from_points(Points, Keys, Values)
Feature from Lines (Python Script 组件)
"""建立 GeoJSON 线数据
Inputs:
Curves: Curves/Polylines you want to export (One branch for each feature). DS:List Access;TH:Default
Keys: Keys to be save in object properties (One branch per feature). DS:List Access;TH:str
Values: Values to save in object properties (One branch per feature). DS:List Access;TH:str
Output:
Features: Strings containing GeoJSON geometry features (not a complete GeoJSON FeatureCollection yet, merge them via Join GeoJSON component). """
ghenv.Component.Name = "Feature from Lines"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "Feature from Lines"
ghenv.Component.Description = """Converts curves/polylines into GeoJSON LineStrings and list of curves into MultiLineStrings."""
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Database"
ghenv.Component.AdditionalHelpFromDocStrings = "1"
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
def feature_from_lines(curves, keys, values):
properties = dict(zip(keys, values))
pts = []
for p in curves:
if rs.IsCurve(p):
points = rs.CurvePoints(p)
pts_coordi = [[p.X, p.Y] for p in points]
pts.append(pts_coordi)
geojson_dict_string = (
'{"type":"Feature","geometry":{"type":"MultiLineString","coordinates":%s},"properties":%s}'
% (pts, properties)
)
return geojson_dict_string.replace("'", '"')
if __name__ == "__main__":
if Curves and Keys and Values:
Features = feature_from_lines(Curves, Keys, Values)
Feature from Polygons (Python Script 组件)
"""建立 GeoJSON 多边形数据
Inputs:
Polygons: Closed polylines you want to export (One branch for each feature). . DS:List Access;TH:Default
Keys: Keys to be save in object properties (One branch per feature). DS:List Access;TH:str
Values: Values to save in object properties (One branch per feature). DS:List Access;TH:str
Output:
Features: Strings containing GeoJSON geometry features (not a complete GeoJSON FeatureCollection yet, merge them via Join GeoJSON component). """
ghenv.Component.Name = "Feature from Polygons"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "Feature from Polygons"
ghenv.Component.Description = """Converts closed polylines into GeoJSON Polygons and lists of closed polylines into MultiPolygons.Doesn't allow creation shapes with holes.If you need shapes with inner holes, use Complex Polygons component instead."""
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Database"
ghenv.Component.AdditionalHelpFromDocStrings = "1"
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
def feature_from_polygons(polygons, keys, values):
properties = dict(zip(keys, values))
pts = []
for p in polygons:
if rs.IsPolyline(p):
points = rs.PolylineVertices(p)
pts_coordi = [[p.X, p.Y] for p in points]
pts.append(pts_coordi)
"""
geojson_dict={
"type":"Feature",
"geometry":{
"type":"MultiPolygon",
"coordinates":[[i] for i in pts]
},
"properties":properties
}
"""
geojson_dict_string = (
'{"type":"Feature","geometry":{"type":"MultiPolygon","coordinates":%s},"properties":%s}'
% ([[i] for i in pts], properties)
)
return geojson_dict_string.replace("'", '"')
if __name__ == "__main__":
if Polygons and Keys and Values:
Features = feature_from_polygons(Polygons, Keys, Values)
Feature from Polygons(+) (Python Script 组件)
"""建立 GeoJSON 多边形(拓扑)数据
Inputs:
Polygons: Closed polylines you want to export (One branch for each feature). DS:List Access;TH:Default
Keys: Keys to be save in object properties (One branch per feature). DS:List Access;TH:str
Values: Values to save in object properties (One branch per feature). DS:List Access;TH:str
Output:
Features: Strings containing GeoJSON geometry features (not a complete GeoJSON FeatureCollection yet, merge them via Join GeoJSON component). """
ghenv.Component.Name = "Feature from Polygons(+)"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "Feature from Polygons(+)"
ghenv.Component.Description = """Converts list of closed polylines into GeoJSON Polygon object with first curve as an outer-ringand all other curves as inner-holes in the shape.Doesn't allow creation of MultiPolygons, for that try 'simple' Polygon to Feature component instead."""
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Database"
ghenv.Component.AdditionalHelpFromDocStrings = "1"
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
def feature_from_polygons_topology(polygons, keys, values):
properties = dict(zip(keys, values))
pts = []
for p in polygons:
if rs.IsPolyline(p):
points = rs.PolylineVertices(p)
pts_coordi = [[p.X, p.Y] for p in points]
pts.append(pts_coordi)
geojson_dict_string = (
'{"type":"Feature","geometry":{"type":"Polygon","coordinates":%s},"properties":%s}'
% (pts, properties)
)
return geojson_dict_string.replace("'", '"')
if __name__ == "__main__":
if Polygons and Keys and Values:
Features = feature_from_polygons_topology(Polygons, Keys, Values)
Join GeoJSON (Python Script 组件)
"""合并各个类型的 GeoJSON 数据
Inputs:
Features: List of complete GeoJSON strings or separate Feature strings to merge. DS:List Access;TH:Default
Output:
GeoJSON: Merged GeoJSON string. """
ghenv.Component.Name = "Join GeoJSON"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "Join GeoJSON"
ghenv.Component.Description = """Merges multiple GeoJSON strings."""
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Database"
ghenv.Component.AdditionalHelpFromDocStrings = "1"
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
def join_geojson(features):
features_ = ",".join(features)
geojson_string = '{"type":"FeatureCollection","features":[%s]}' % (
features_
)
return geojson_string
if __name__ == "__main__":
if Features:
GeoJSON = join_geojson(Features)
``Write File` (Python Script 组件)
"""本地保存 GeoJSON 数据
Inputs:
Directory: Path to the directory where files will be created. . DS:Item Access;TH:str
Filename: Name of the file.The suffix name is geojson. DS:Item Access;TH:str
Data: Text data you want to save. DS:Item Access;TH:str
Run: Needs to be True for the file to be created. DS:Item Access;TH:bool
Overwrite: Existing files will be overwritten only when this is True. DS:Item Access;TH:bool
Output:
fp:the file path"""
ghenv.Component.Name = "Write File"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "Write File"
ghenv.Component.Description = """Writes text data to a file on your computer."""
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Database"
ghenv.Component.AdditionalHelpFromDocStrings = "1"
import os
def string2file(directory, filename, data, overwrite=False):
fp = os.path.join(directory, filename + ".geojson")
if os.path.exists(fp):
print("File exists.")
if overwrite:
with open(fp, "w") as f:
f.writelines(data)
print("GeoJson has dumped.")
else:
with open(fp, "w") as f:
f.writelines(data)
print("GeoJson has dumped.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
if Directory and Filename and Data:
if Run:
string2file(Directory, Filename, Data, Overwrite)
fp = os.path.join(Directory, Filename + ".geojson")
2.6.2.4 在 Python 中读取 Python Script 存储的 GeoJSON 数据
为了检验 Python Script 中写入 GeoJSON 数据的有效性,在 Python 中书写验证测试代码结果如图 2.6-7_1-4。
- 读取 GeoJSON 数据为 GeoDataFrame 格式数据,打印查看数据内容,包括属性字段和
geometry几何列; - 打印查看投影坐标 CRS(epsg),投影默认配置为 4326,并未修正(注意,为错误投影);
- 打印显示几何对象,确认几何图形正确。
验证测试代码:
import geopandas as gpd
if __name__=="__main__":
testing_fn = r"../data/geojson_testing.geojson"
testing = gpd.read_file(testing_fn)
print(testing)
print(testing.crs)
a=testing['geometry'][0]
b=testing['geometry'][1]
c=testing['geometry'][2]
d=testing['geometry'][3]
计算结果:
Lable ID geometry
0 building group_1 2 MULTIPOLYGON (((526.00000 141.00000, 561.00000...
1 building group_2 3 POLYGON ((523.00000 165.00000, 518.00000 193.0...
2 boundary pts 0 MULTIPOINT (350.96110 50.01127, 346.94704 190....
3 generate buildings 1 MULTILINESTRING ((355.57978 82.23316, 365.5215...
epsg:4326
| a | b | c | d |
|---|---|---|---|
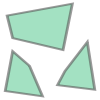
图 2.6-7_1 写入的多边形 |

图 2.6-7_2 写入的多边形(拓扑) |
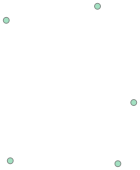
图 2.6-7_3 写入的点 |
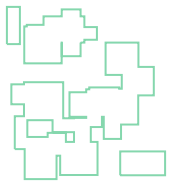
图 2.6-7_4 写入的线 |
注释(Notes):
① SQLite,是一个 C 语言库,实现了一个小型、快速、自包含( self-contained)、高可靠性、全功能的 SQL 数据库引擎(https://www.sqlite.org/index.html)。
② PostgreSQL,为开源的关系型数据库。经过近40年的发展,在可靠性、功能健壮性和性能方面具有优秀的表现(https://www.postgresql.org/)。
③ Anaconda,是用于科学计算(数据科学、机器学习应用、大规模数据处理、预测分析等)的 Python 和 R 编程语言软件平台,旨在简化包的管理和部署(https://www.anaconda.com/)。
④ 百度智能云,(https://login.bce.baidu.com/)。
⑤ DB Browser for SQLite(DB4S),是一个用于创建、搜索和编辑 SQLite 数据库文件,可视化的开源工具(https://sqlitebrowser.org/)。
⑥ QGIS,空间可视化和决策工具(https://www.qgis.org/)。
⑦ pgAdmin,开源数据库 PostgreSQL 的开源管理和开发平台 (https://www.pgadmin.org/)。
⑧ Chicago Data Portal,芝加哥数据门户(https://data.cityofchicago.org/)。
⑨ Googel Earth Pro,(https://earth.google.com/intl/earth/versions/)。
⑩ GeoJSON 数据格式,是基于 Json,用于表示简单地理特征及其非空间属性的标准格式(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GeoJSON)。