2.7.3 智能体
Created on 2024-10-02T11:23:03+08:00 @author: Richie Bao
基于智能体(代理)的模型(Agent-Based Models,ABM)是用于模拟定义环境中各个智能体交互作用的模型,其中每个智能体都基于一组规则动作,这些规则包括行为、决策过程及与其他智能体或环境的交互,通常用于诸如生态学、经济学、社会学和城市规划等领域复杂系统的研究,探索系统中个体行为的宏观涌现。研究复杂系统的一个重要机构是圣菲研究所( Santa Fe Institute,SFI) ①,成立于1984年,探索理解物理、生物、社会、文化、技术、甚至可能的天体生物学中潜在、共有的模式,揭示这些不断演变的世界中看不见的机制和运作过程。1986 年 G.尼科里斯和I.普利高津出版了专著《探索复杂性》[1]。复杂性研究从传统科学领域拓展到生物学、经济学、人工智能、计算机科学、生命科学等领域,出现蝴蝶效应、非线性、临界、协同、混沌、自组织和涌现等新思想。而复杂性科学与计算机科学互为推动,复杂适应系统理论之父约翰•霍兰德(John Henry Holland)在其研究遗传算法之初使用计算机进行数学模型的建立,而遗传算法也成为了人工智能开发的重要理论基础。ABM 模拟实现需要计算机建模系统,广泛使用的一个工具为NetLogo②,是一个多智能体(代理)可编程建模环境(multi-agent programmable modeling environment),被世界上成千上万的学生、教师和研究者使用。NetLogo 的模型库集成了大量多领域的示例模型,涉及艺术、生物、化学和物理、计算机科学、地球科学、游戏、数学、网络、哲学、心理学、社会科学、系统动力学和城市规划等众多领域的探索研究,为各个方向的研究者提供了第一手的参考材料。因为 Python 语言的不断发展,其扩展库的不断增加,尤其 Numpy、Pandas、Scipy 等数据分析和科学计算库的完善,及 scikit-learn 机器学习和 Pytorch、TensorFlow 等深度学习库对 AI 智能领域理论方法的集成和探索,为应用 Python 完善的生态系统研究 ABM 提供了更多的可能性。基于 Python 编程语言 ABM 的主要支持库有Mesa③ 和Repast4Py ④等。Repast4Py 可以在 Windows 上运行,但是因为需要预安装 MPI(Message Passing Interface)⑤并支持mpi4py⑥,且 Repast4Py 在 Linux 上开发和测试,更适合于在 Linux 上运行,因此本章试验使用 Mesa 库。Mesa 库⑦的贡献者至少有 131 人,使用者超过 1.7k 人,并不断完善更新,持续维护中。
2.7.3.1 NetLogo 下的 Urban Suite - Pollution 模型
以 Netlogo 的 Urban Suite - Pollution,USP⑧模型为试验对象[2],说明在 Mesa(Python) 和在 Pyton Script(GH) 中的实现方法。USP 模型是对捕食者-猎物生态系统(predator-prey ecosystem)脆弱平衡(fragile equilibrium )检验智能体模型,包括 People(人)、Tree(树木,景观要素)智能体,和 Patch/Pollution (发电厂,空气污染物)环境之间的相互作用。USP 模型可以探索随时间推移种群之间的相互作用行为,即捕食者(污染)和猎物(人)在多次迭代中表现出的种群数变化,并以人口规模(智能体 People 种群数)的规律振荡(周期)表明生态系统的平衡稳定。在迭代过程中,人口规模虽然有波动,但随时间推移,人口仍然能保持在一个相对稳定的水平上;而不规律的振荡表明一种不稳定,导致这两个互相依赖的种群可能灭绝,其中捕食者抑制猎物的密度,而猎物刺激捕食者的密度。
NetLogo 语言的学习材料可以从其官网地址获取。
NetLogo 下的 USP 模型结果如图 2.7.3-1,可以从 NetLogo 的模型库(NetLogo Models Library:Curricular Models/Urban Suite)下调出。

图 2.7.3-1 NetLogo 下的 USP 模型结果迭代过程
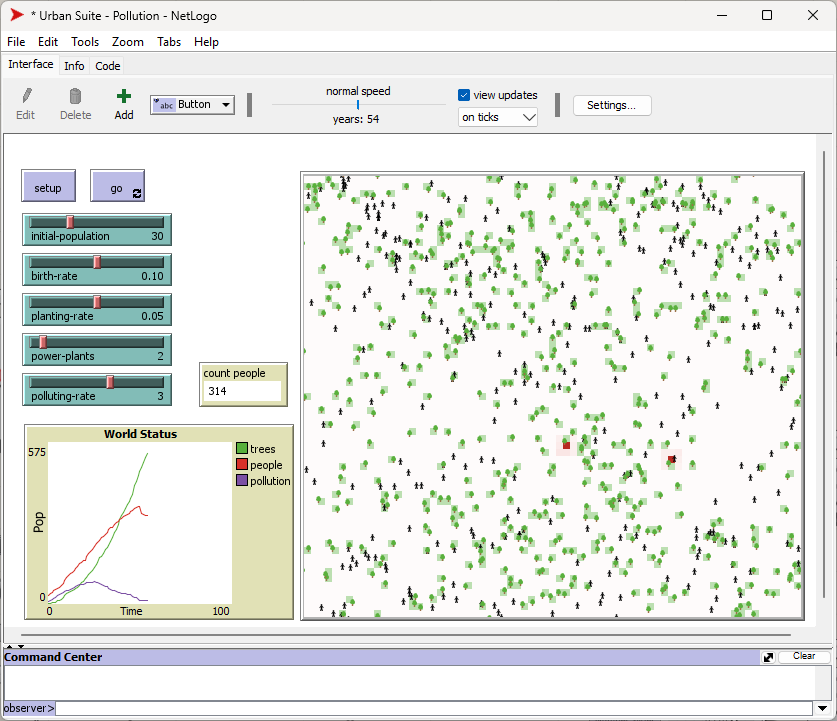
图 2.7.3-1 NetLogo 下的 USP 模拟过程第54个迭代结果
USP 的 NetLogo 模型代码如下:
USP 模型 (NetLogo 代码)
breed [ people person ]
breed [ trees tree ]
turtles-own [ health ]
patches-own [
pollution
is-power-plant?
]
to setup
clear-all
set-default-shape people "person"
set-default-shape trees "tree"
ask patches [
set pollution 0
set is-power-plant? false
]
create-power-plants
ask patches [ pollute ]
create-people initial-population [
set color black
setxy random-pxcor random-pycor
set health 5
]
reset-ticks
end
to go
if not any? people [ stop ]
ask people [
wander
reproduce
maybe-plant
eat-pollution
maybe-die
]
diffuse pollution 0.8
ask patches [ pollute ]
ask trees [
cleanup
maybe-die
]
tick
end
to create-power-plants
ask n-of power-plants patches [
set is-power-plant? true
]
end
to pollute ;; patch procedure
if is-power-plant? [
set pcolor red
set pollution polluting-rate
]
set pcolor scale-color red (pollution - .1) 5 0
end
to cleanup ;; tree procedure
set pcolor green + 3
set pollution max (list 0 (pollution - 1))
ask neighbors [
set pollution max (list 0 (pollution - .5))
]
set health health - 0.1
end
to wander ;; person procedure
rt random-float 50
lt random-float 50
fd 1
set health health - 0.1
end
to reproduce ;; person procedure
if health > 4 and random-float 1 < birth-rate [
hatch-people 1 [
set health 5
]
]
end
to maybe-plant ;; person procedure
if random-float 1 < planting-rate [
hatch-trees 1 [
set health 5
set color green
]
]
end
to eat-pollution ;; person procedure
if pollution > 0.5 [
set health (health - (pollution / 10))
]
end
to maybe-die ;; die if you run out of health
if health <= 0 [ die ]
end
; Copyright 2007 Uri Wilensky.
; See Info tab for full copyright and license.
分析 USP 模型的 NetLogo 代码,配置智能体person和tree,及patches:由create-people initial-population[]程序初始化 person,随机位置放置指定数量的人;tree 一开始并没有栽种;patches属性is-power-plant确定该单元是否有power plant发电厂,由create-power-plants配置指定数量的发电厂。并有pollution属性,表明污染浓度。由to go程序执行迭代,如果 person 智能体减少至无,则停止程序,否则依次执行随机游走(wander),生育(reproduce),种植(maybe-plant),受到污染气体影响降低健康指数(eat-pollution)和如果健康指数(health)等于或小于0则从迭代中移除(代表死亡)(maybe-die)等行为。每种行为对应定义为一个程序;每一迭代中,以发电厂为中心,污染物会发生扩散,由diffuse pollution 0.8语句实现。并执行程序pollute,配置发电厂位置的pollution属性值;对智能体trees,依次执行吸收净化污染物(cleanup),如果树木健康值小于或等于0则树木死亡(maybe-die)的行为。
2.7.3.2 Meta(Python) 重写 NetLogo 下的 USP 模型
虽然 ChatGPT⑨目前直接将 NetoLogo 代码转换为使用 Mesa 库③的 Python 代码比较粗糙,但是已经可以大幅度的提升代码迁移的效率。为了使得代码的结构清晰,按照agents(智能体)、model(模型)、server(服务端)三个主要结构建立模块,分别为各个智能体每一迭代下的行为,模型的基本配置和初始化,及在服务端口发布模型,可以运行查看过程和结果,包括必要的动态分析图表等。USP 模型在 Mesa 中实现的结果如图 2.7.3-2。

图 2.7.3-2 Mesa 下的 USP 模型结果迭代过程
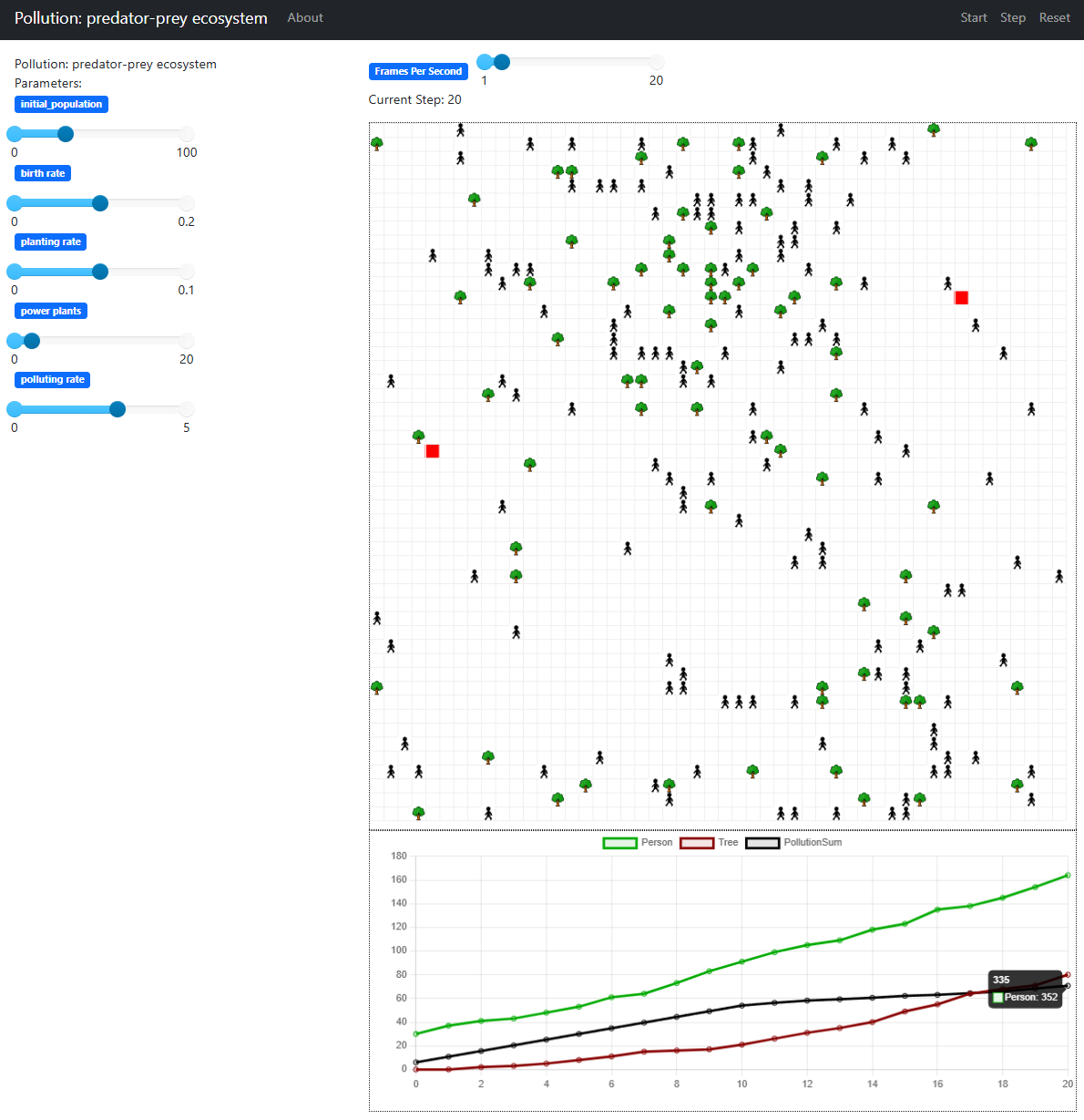
图 2.7.3-2 Mesa 下的 USP 模拟过程第20个迭代结果
NetLogo 中,智能体在二维空间中运动的命令forward (fd)、 left (lt)和right (rt)在 Mesa 库中没有直接的对应方法,通过定义Movement类实现,方便 NetLogo 代码的转换。在迁移中尽量保持变量和类、函数方法名与 NetLogo 源码保持一致,例如智能体定义为类Person、Tree和Patch,并继承父类mesa.Agent,其中Person的行为(方法)有wander()、reproduce()、maybe_plant()、eat_pollution()和maybe_die()等;Tree的行为(方法)有cleanup()和maybe_die();用Patch存储环境信息,具有pollution和is_power_plant等属性。
agents.py (Python 代码)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Sep 28 22:03:07 2024
@author: richie bao
"""
import mesa
import numpy as np
import math
class Movement:
@staticmethod
def rt(heading, angle):
"""按给定的角度(度)向右转"""
return (heading + angle) % 360
@staticmethod
def lt(heading, angle):
"""按给定的角度(度)向左转"""
return (heading - angle) % 360
@staticmethod
def fd(agent, pos, heading, model, distance=1, torus=True):
"""沿航向方向按给定距离向前移动"""
# 将航向度转换为弧度用于三角计算
heading_rad = math.radians(heading)
# 根据航向计算新位置
new_x = pos[0] + distance * math.cos(heading_rad)
new_y = pos[1] + distance * math.sin(heading_rad)
# 将新位置转换为整数网格位置
new_pos = (round(new_x), round(new_y))
# 确保新位置在网格边界内
if torus:
model.grid.move_agent(agent, new_pos)
else:
if model.grid.out_of_bounds(new_pos):
print(
f"New position {new_pos} is out of bounds. Movement ignored."
)
else:
# 移动智能体到新位置
model.grid.move_agent(agent, new_pos)
class Person(mesa.Agent):
def __init__(self, unique_id, pos, model, health=5, heading=0):
super().__init__(unique_id, model)
self.pos = pos
self.heading = heading
self.health = health
def step(self):
self.wander()
self.reproduce()
self.maybe_plant()
self.eat_pollution()
self.maybe_die()
def wander(self):
self.heading = Movement.rt(self.heading, self.random.uniform(0, 50))
self.heading = Movement.lt(self.heading, self.random.uniform(0, 50))
Movement.fd(self, self.pos, self.heading, self.model, distance=1)
self.health -= 0.1
def reproduce(self):
if self.health > 4 and self.random.random() < self.model.birth_rate:
new_person = Person(
self.model.next_id(),
self.pos,
self.model,
5,
self.random.uniform(0, 360),
)
self.model.grid.place_agent(new_person, self.pos)
self.model.schedule.add(new_person)
def maybe_plant(self):
if self.random.random() < self.model.planting_rate:
new_tree = Tree(
self.model.next_id(), self.pos, self.model, health=5
)
self.model.grid.place_agent(new_tree, self.pos)
self.model.schedule.add(new_tree)
def eat_pollution(self):
cell_content = self.model.grid.get_cell_list_contents([self.pos])
patch = next(filter(lambda x: isinstance(x, Patch), cell_content), None)
if patch and patch.pollution > 0.5:
self.health -= patch.pollution / 10
def maybe_die(self):
if self.health <= 0:
self.model.grid.remove_agent(self)
self.model.schedule.remove(self)
class Tree(mesa.Agent):
def __init__(self, unique_id, pos, model, health=5):
super().__init__(unique_id, model)
self.pos = pos
self.health = health
def step(self):
self.cleanup()
self.maybe_die()
def cleanup(self):
cell_content = self.model.grid.get_cell_list_contents([self.pos])
patch = next(filter(lambda x: isinstance(x, Patch), cell_content), None)
if patch:
patch.pollution = max(0, patch.pollution - 1)
self.health -= 0.1
for neighbor in self.model.grid.get_neighbors(self.pos, moore=True):
if isinstance(neighbor, Patch):
neighbor.pollution = max(0, neighbor.pollution - 0.5)
def maybe_die(self):
if self.health <= 0:
self.model.grid.remove_agent(self)
self.model.schedule.remove(self)
class Patch(mesa.Agent):
def __init__(
self, unique_id, pos, model, pollution=0, is_power_plant=False
):
super().__init__(unique_id, model)
self.pos = pos
self.pollution = 0
self.is_power_plant = False
def step(self):
self.pollute_diffusion()
def pollute_diffusion(self):
if self.is_power_plant:
neighbors = self.model.grid.get_neighborhood(
self.pos, moore=True, include_center=False
)
for neighbor in neighbors:
this_cell = self.model.grid.get_cell_list_contents([neighbor])
for obj in this_cell:
if isinstance(obj, Patch):
obj.pollution += (
self.pollution * 0.8 / 8
) # 扩散速率
# self.pollution -= self.pollution * 0.8 # 降低当前单元的污染浓度值
为了方便计算一个单元包含多个智能体(MultiGrid)情况下,所有单元中各个智能体的总数,定义RandomActivationByTypeFiltered类,位于scheduler模块下。
scheduler.py (Python 代码)
from typing import Callable, Optional, Type
import mesa
class RandomActivationByTypeFiltered(mesa.time.RandomActivationByType):
"""
重写 get_type_count 方法的调度器(scheduler),允许在计数之前由函数删选待计数的智能体
示例:
>>> scheduler = RandomActivationByTypeFiltered(model)
>>> scheduler.get_type_count(AgentA, lambda agent: agent.some_attribute > 10)
"""
def get_type_count(
self,
type_class: Type[mesa.Agent],
filter_func: Optional[Callable[[mesa.Agent], bool]] = None,
) -> int:
"""
返回队列中满足筛选条件,特定类型智能体的当前数目
"""
if type_class not in self.agents_by_type:
return 0
count = 0
for agent in self.agents_by_type[type_class].values():
if filter_func is None or filter_func(agent):
count += 1
return count
model模块包含模型参数的基本配置,包括环境高宽,height和width,初始化的Person智能体数initial_population,出生率birth_rate,植树率planting_rate,和发电厂数power_plants,及其污染浓度polluting_rate等;并包括智能体初始化,继承父类mesa.Model。mesa.DataCollector()方法可以收集模型级(model-)、智能体级(agent-)和智能体类型级(agent-type-level)变量值,以字典的形式存储。并定义create_power_plants()方法配置patch的is_power_plant属性值,声明单元包含由发电厂。
model.py (Python 代码)
import mesa
from scheduler import RandomActivationByTypeFiltered
from agents import Person, Tree, Patch
import numpy as np
import warnings
warnings.simplefilter("ignore", category=Warning)
class PollutionModel(mesa.Model):
height = 50
width = 50
initial_population = 30
birth_rate = 0.1
planting_rate = 0.05
power_plants = 2
polluting_rate = 3
def __init__(
self,
height=50,
width=50,
initial_population=30,
birth_rate=0.1,
planting_rate=0.05,
power_plants=2,
polluting_rate=3,
):
super().__init__()
self.height = height
self.width = width
self.polluting_rate = polluting_rate
self.birth_rate = birth_rate
self.planting_rate = planting_rate
self.initial_population = initial_population
self.power_plants = power_plants
self.grid = mesa.space.MultiGrid(self.width, self.height, torus=True)
self.schedule = RandomActivationByTypeFiltered(self)
self.datacollector = mesa.DataCollector(
{
"Person": lambda m: m.schedule.get_type_count(Person),
"Tree": lambda m: m.schedule.get_type_count(Tree),
"PollutionSum": lambda m: sum(
[
a.pollution
for a in m.schedule.agents_by_type[Patch].values()
]
),
}
)
for agent, (x, y) in self.grid.coord_iter():
patch = Patch(self.next_id(), (x, y), self)
self.grid.place_agent(patch, (x, y))
self.schedule.add(patch)
for _ in range(self.initial_population):
x, y = self.random_xy()
person = Person(
self.next_id(), (x, y), self, 5, self.random.uniform(0, 360)
)
self.grid.place_agent(person, (x, y))
self.schedule.add(person)
self.create_power_plants(self.power_plants)
self.running = True
self.datacollector.collect(self)
def create_power_plants(self, power_plants):
xy_lst = []
for _ in range(power_plants):
xy_lst.append(self.random_xy())
cells = self.grid.get_cell_list_contents(xy_lst)
patches = [patch for patch in cells if isinstance(patch, Patch)]
for p in patches:
p.is_power_plant = True
p.pollution = self.polluting_rate
def random_xy(self):
x = self.random.randrange(self.grid.width)
y = self.random.randrange(self.grid.height)
return (x, y)
def step(self):
self.schedule.step()
self.datacollector.collect(self)
server模块用于配置智能体模拟窗口和可视化元素及图表等,包括窗口名称、参数说明、关于模型等文字信息;模型参数值输入,例如使用滑条,下拉菜单等;配置智能体图标,如图 2.7.3-2 中的人形和树木;并使用mesa.DataCollector()方法收集的数据建立可视化图表,方便观察数据变化。
server.py (Python 代码)
import mesa
from agents import Person, Tree, Patch
from model import PollutionModel
import matplotlib.colors as colors
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.cm as cm
_COLORS4Patch = {
True: "Red",
False: "white",
}
_COLORS4WorldStatus = {
"Person": "#00AA00",
"Tree": "#880000",
"PollutionSum": "#000000",
}
def pollution_portrayal(agent):
if agent is None:
return
if type(agent) is Patch:
portrayal = {
"Shape": "rect",
"w": 1,
"h": 1,
"Filled": "true",
"Layer": 0,
}
portrayal["x"] = agent.get_row()
portrayal["y"] = agent.get_col()
portrayal["Color"] = _COLORS4Patch[agent.get_state()]
if type(agent) is Person:
portrayal = {
"Shape": "./shapes/person.png",
"w": 1,
"h": 1,
"Filled": "true",
"Layer": 1,
}
portrayal["Color"] = "Olive"
if type(agent) is Tree:
portrayal = {
"Shape": "./shapes/tree.png",
"w": 1,
"h": 1,
"Filled": "true",
"Layer": 1,
}
portrayal["Color"] = "Green"
return portrayal
worldStatus_chart = mesa.visualization.ChartModule(
[
{"Label": label, "Color": color}
for (label, color) in _COLORS4WorldStatus.items()
]
)
model_params = {
"title": mesa.visualization.StaticText(
"Pollution: predator-prey ecosystem"
),
"parameters": mesa.visualization.StaticText("Parameters:"),
"initial_population": mesa.visualization.Slider(
"initial_population", 30, 0, 100
),
"birth_rate": mesa.visualization.Slider("birth rate", 0.1, 0, 0.2, 0.01),
"planting_rate": mesa.visualization.Slider(
"planting rate", 0.05, 0, 0.1, 0.01
),
"power_plants": mesa.visualization.Slider("power plants", 2, 0, 20),
"polluting_rate": mesa.visualization.Slider("polluting rate", 3, 0, 5),
}
canvas_element = mesa.visualization.CanvasGrid(
pollution_portrayal, 50, 50, 862, 862
)
server = mesa.visualization.ModularServer(
PollutionModel,
[canvas_element, worldStatus_chart],
"Pollution: predator-prey ecosystem",
model_params,
)
server.port = 8523
server.launch(open_browser=True)
运行server模块,会弹出端口为server.port = 8523的网页(http://127.0.0.1:8523/),显示图 2.7.3-2 窗口,点击Start可以执行模拟,Step逐次迭代,Reset重设环境。
2.7.3.3 GH(Python Script) 下实现 USP 模型
在 GH 下并不用从底层构建类似 NetLogo 和 Mesa 的工具,而直接在 GH 的 Python 环境下(C:\Users\user\.rhinocode\py39-rh8)安装 Mesa 库(pip install mesa),调用 Mesa 的方法,在 Python Script(GH) 下实现 USP 模型。因为已经使用 Mesa 库用 Python 编程语言实现了 USP 模型,将其迁移到 GH 下转换为组件的节点式可视化编程的方式,只需要引出输入端和输出端参数,并用 GH(Rhino) 下的图形可视化方式表达图形界面,因此仅需要稍加调整就可完成代码到 GH 下的迁移,结果如图 2.7.3-3。

图 2.7.3-3 GH(Python Script) 下的 USP 模型结果迭代过程
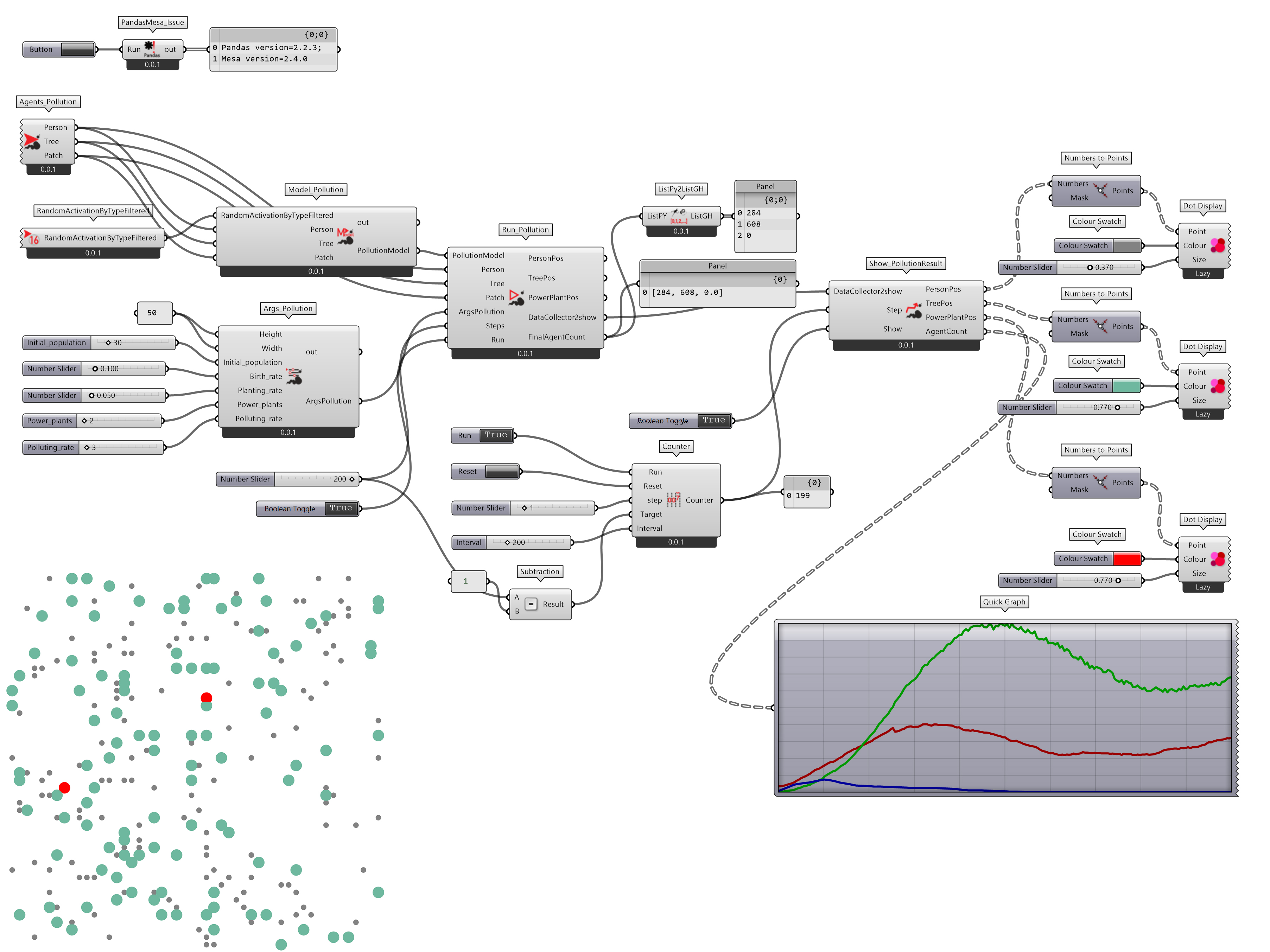
图 2.7.3-3 GH(Python Script)下的 USP 模拟过程第25个迭代结果及执行代码
GH 下的 USP 模型保持agents、model的模块,对应组件Agents_Pollution、Model_Pollution;将server模块对应转换为Run_Pollution和可用于可视化图形数据提取组件Show_PollutionResult;将scheduler模块写入组件RandomActivationByTypeFiltered;为了简化组件输入端,方便参数值输入,可以将输入参数单独定义为一个组件,如Args_Pollution。定义的 GH 组件结果如图2.7.3-4。
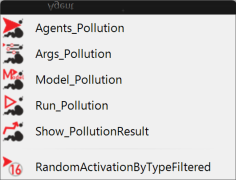
图 2.7.3-4 USP 模型实现组件
Python 的 Mesa 库的依赖库包含 Pandas 库,而 RH 8 SR10 版本的 GH 安装 Python 库 Pandas 存在库冲突。调入 Pandas 时,提示 partially initialized module ‘pandas’ has no attribute ‘_pandas_datetime_CAPI’等错误信息,因此定义 PandasMesa_Issue 组件。如果 Python Script 组件存在调入 Pandas 时提示错误的情况,可以尝试运行该组件。运行前一般执行 RH -> Tools -> Script -> Edit -> Tools -> Advanced -> Reset Python 3 (CPython) Runtime。
PandasMesa_Issue (Python Script 组件)
ghenv.Component.Name = "PandasMesa_Issue"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "PandasMesa_Issue"
ghenv.Component.Description = "解决 Pandas 库冲突(临时性)"
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Util"
ghenv.Component.PanelSection = 3
#! python3
#r: pandas, openpyxl, psycopg2, mesa
# requirements: pandas
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import scriptcontext as sc
import System
import System.Collections.Generic
import Rhino
import locale
locale.setlocale(locale.LC_ALL, 'en_US')
import openpyxl
import psycopg2
import pandas as pd
import mesa
print(f"Pandas version={pd.__version__};\nMesa version={mesa.__version__}")
Agents_Pollution组件基本原封不动的迁移了agents模块,只是引出了输出端Person、Tree和Patch,对应三个智能体的类。(代码中显示的给出了Person = Person等语句,因为输出端变量名同,因此可以省略该部分代码)
Agents_Pollution (Python Script 组件)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
捕食者-猎物生态系统(predator-prey ecosystem)脆弱平衡(fragile equilibrium )检验智能体模型。
Output:
Person: Class
智能体对象 Person,人
Tree: Class
智能体对象 Tree, 树木
Patch: Class
智能体对象 Patch,如果属性 is_power_plant 为 True,则表示存在发电厂;并有属性 pollution,记录污染浓度
"""
import mesa
import numpy as np
import math
ghenv.Component.Name = "Agents_Pollution"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "Agents_Pollution"
ghenv.Component.Description = "生态系统脆弱平衡检验智能体模型——智能体对象"
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Agent"
ghenv.Component.PanelSection = 1
class Movement:
class Person(mesa.Agent):
class Tree(mesa.Agent):
class Patch(mesa.Agent):
if __name__ == "__main__":
Person = Person
Tree = Tree
Patch = Patch
RandomActivationByTypeFiltered组件基本原封不动的迁移于scheduler模块。
RandomActivationByTypeFiltered (Python Script 组件)
from typing import Callable, Optional, Type
import mesa
ghenv.Component.Name = "RandomActivationByTypeFiltered"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "RandomActivationByTypeFiltered"
ghenv.Component.Description = "指定智能体类型,计数智能体"
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Agent"
ghenv.Component.PanelSection = 1
class RandomActivationByTypeFiltered(mesa.time.RandomActivationByType):
if __name__=="__main__":
RandomActivationByTypeFiltered=RandomActivationByTypeFiltered
Model_Pollution组件基本原封不动的迁移于model模块。
Model_Pollution (Python Script 组件)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
捕食者-猎物生态系统(predator-prey ecosystem)脆弱平衡(fragile equilibrium )检验智能体模型。
Inputs:
RandomActivationByTypeFiltered: Class
计数指定的智能体类型
Person: Class
智能体 Person(人)
Tree: Class
智能体 Tree(树木)
Patch: Class
智能体 Patch(如果其属性 is_power_plant 为 True,则表示存在发电厂)
Output:
PollutionModel: Class
生态系统脆弱平衡模型
"""
import mesa
import numpy as np
import warnings
warnings.simplefilter("ignore", category=Warning)
ghenv.Component.Name = "Model_Pollution"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "Model_Pollution"
ghenv.Component.Description = "生态系统脆弱平衡检验智能体模型——模型"
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Agent"
ghenv.Component.PanelSection = 1
class PollutionModel(mesa.Model):
if __name__ == "__main__":
PollutionModeln = PollutionModel
Args_Pollution组件,仅有一行代码ArgsPollution=[Height,Width,Initial_population,Birth_rate,Planting_rate,Power_plants,Polluting_rate],其目的只是为了简化Run_Pollution组件的输入端参数,而将参数部分单独定义为一个组件。
Args_Pollution (Python Script 组件)
'''
捕食者-猎物生态系统(predator-prey ecosystem)脆弱平衡(fragile equilibrium )检验智能体模型输入参数
'''
ghenv.Component.Name = "Args_Pollution"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "Args_Pollution"
ghenv.Component.Description = "生态系统脆弱平衡检验智能体模型——参数"
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Agent"
ghenv.Component.PanelSection = 1
ArgsPollution=[Height,Width,Initial_population,Birth_rate,Planting_rate,Power_plants,Polluting_rate]
Run_Pollution组件运行智能体模型并收集迭代过程数据。因为 GH 组件的设计是完成组件内的程序运行后,再输出结果到输出端,因此不能实时传输过程数据结果。只有收集所有过程数据后,再现已经计算的过程。而为了达到收集过程数据的目的,定义变量dataCollector2show,以字典的形式收集每一迭代下智能体Person和Tree的数量(种群数)personCount和treeCount,智能体Patch属性值pollution污染浓度和pollusionSum,及智能体的变化位置personPos、treePos和工厂位置powerPlantPos,并作为参数由输出端DataCollector2show输出。因为输出端输出的并非 GH 基本的数据结构,为了正确输出 Python 的 Dict(字典)数据类型,需要在组件上Shift+右键的高级弹出菜单中勾选Avoid Marshalling Outputs选项,避免组件自动转化为 GH 类型,而出现错误。
Run_Pollution (Python Script 组件)
"""
运行捕食者-猎物生态系统(predator-prey ecosystem)脆弱平衡(fragile equilibrium )检验智能体模型。
Input:
PollutionModel:Class
生态系统脆弱平衡模型
Person: Class
智能体 Person(人)
Tree: CLass
智能体 Tree(树木)
Patch:
智能体 Patch,含有属性 is_power_plant 和 pollution
ArgsPollution: List
模型参数配置
Steps: Item; int
迭代次数
Run: Item; Bool
运行
Output:
PersonPos: Tree;Point
智能体 Person 位置坐标
TreePos: Tree;Point
智能体 Tree 位置坐标
PowerPlantsPos: Tree; Points
智能体 Patch(PowerPlant) 位置坐标
DataCollector2show:Dict
记录有每一迭代下智能体计算变量值:personCount,treeCount,pollusionSum(污染浓度和);及智能体位置参数:personPos,treePos 和 powerPlantPos
FinalAgentCount: List
每一迭代智能体计数
"""
import ghpythonlib.treehelpers as th
import Grasshopper as gh
ghenv.Component.Name = "Run_Pollution"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "Run_Pollution"
ghenv.Component.Description = "生态系统脆弱平衡检验智能体模型——模型"
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Agent"
ghenv.Component.PanelSection = 1
if ArgsPollution:
(
Height,
Width,
Initial_population,
Birth_rate,
Planting_rate,
Power_plants,
Polluting_rate,
) = ArgsPollution
if Run:
dataCollector2show = {}
model = PollutionModel(
Height,
Width,
Initial_population,
Birth_rate,
Planting_rate,
Power_plants,
Polluting_rate,
)
for i in range(Steps):
personCount = model.schedule.get_type_count(Person)
treeCount = model.schedule.get_type_count(Tree)
pollusionSum = sum(
[
agent.pollution
for agent in model.schedule.agents_by_type[Patch].values()
]
)
personPos = [
[agent.pos[0], agent.pos[1], 0]
for agent in model.schedule.agents
if isinstance(agent, Person)
]
PersonPos = th.list_to_tree(personPos)
treePos = [
[agent.pos[0], agent.pos[1], 0]
for agent in model.schedule.agents
if isinstance(agent, Tree)
]
TreePos = th.list_to_tree(treePos)
powerPlantPos = [
[agent.pos[0], agent.pos[1], 0]
for agent in model.schedule.agents
if isinstance(agent, Patch) and agent.is_power_plant
]
PowerPlantPos = th.list_to_tree(powerPlantPos)
dataCollector2show[i] = [
personCount,
treeCount,
pollusionSum,
personPos,
treePos,
powerPlantPos,
]
model.step()
DataCollector2show = dataCollector2show
FinalAgentCount = [personCount, treeCount, pollusionSum]
Show_PollutionResult组件是提取Run_Pollution收集的计算过程参数值,转化为 GH 数据格式输出,用于结果的可视化。
Show_PollutionResult (Python Script 组件)
"""
绘制捕食者-猎物生态系统(predator-prey ecosystem)脆弱平衡(fragile equilibrium )检验智能体模型计算结果。
Inputs:
DataCollector2show: Dict
记录有每一迭代下智能体计算变量值:personCount,treeCount,pollusionSum(污染浓度和);及智能体位置参数:personPos,treePos 和 powerPlantPos
Step:Item; int
迭代数
Show: Item; bool
是否显示
Output:
PersonPos: Tree;Point
指定迭代区间智能体 Person 位置坐标
TreePos: Tree;Point
指定迭代区间智能体 Patch(PowerPlant) 位置坐标
PowerPlantsPos: Tree; Points
指定迭代区间智能体 Patch(PowerPlant) 位置坐标
AgentCount: Tree; int
指定迭代区间指定迭代区间智能体计数
"""
import ghpythonlib.treehelpers as th
import numpy as np
ghenv.Component.Name = "Show_PollutionResult"
ghenv.Component.NickName = "Show_PollutionResult"
ghenv.Component.Description = (
"生态系统脆弱平衡检验智能体模型——统计结果绘制变量值"
)
ghenv.Component.Message = "0.0.1"
ghenv.Component.Category = "Moths"
ghenv.Component.SubCategory = "Agent"
ghenv.Component.PanelSection = 1
if Step is None:
Step = 3
if Show and DataCollector2show:
_, _, _, personPos, treePos, powerPlantPos = DataCollector2show[Step]
PersonPos = th.list_to_tree(personPos)
TreePos = th.list_to_tree(treePos)
PowerPlantPos = th.list_to_tree(powerPlantPos)
agentCount = []
for i in range(Step):
personCount, treeCount, pollusionSum, _, _, _ = DataCollector2show[i]
agentCount.append([personCount, treeCount, pollusionSum])
agentCount_T = np.array(agentCount).T.tolist()
AgentCount = th.list_to_tree(agentCount_T)
ListPy2ListGH组件仅包括一行代码ListGH=ListPY,用 GH 组件自动转化为 GH 数据类型的功能,实现将 Python 列表(List)转化为 GH 列表的数据形式。
GH 下 USP 模型运行模拟的可视化过程包括智能体位置变化和智能体数量变化曲线两部分。第一部分结合使用Counter组件(1.3.2 部分定义)动态观察智能体的位置变化;而曲线部分则使用Quick Graph组件实现。
注释(Notes):
① 圣菲研究所( Santa Fe Institute),(https://www.santafe.edu)。
② NetLogo,(https://ccl.northwestern.edu/netlogo/models/)。
③ Mesa,(https://mesa.readthedocs.io/stable/index.html)。
④ Repast for Python (Repast4Py),(https://repast.github.io/repast4py.site/guide/user_guide.html#_getting_started)。
⑤ MPI(Message Passing Interface),(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_MPI)。
⑥ mpi4py,(https://mpi4py.readthedocs.io/en/stable)。
⑦ Mesa 库,GitHub 代码托管仓库地址,(https://github.com/projectmesa/mesa)。
⑧ Urban Suite - Pollution,USP,(https://ccl.northwestern.edu/netlogo/models/UrbanSuite-Pollution)。
⑨ ChatGPT,是 OpenAI 公司开发的生成式人工智能(generative artificial intelligence,GAI)聊天机器人(https://openai.com/chatgpt/)。
参考文献:
[1] G.尼科里斯,I.普利高津著.罗久里,陈奎宁译. 探索复杂性[M].四川:四川教育出版社.2010.4.
[2] Felsen, M. and Wilensky, U. (2007). NetLogo Urban Suite - Pollution model. http://ccl.northwestern.edu/netlogo/models/UrbanSuite-Pollution. Center for Connected Learning and Computer-Based Modeling, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL.